Proteasome gene expression is controlled by coordinated functions of multiple transcription factors
- PMID: 38767572
- PMCID: PMC11104393
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202402046
Proteasome gene expression is controlled by coordinated functions of multiple transcription factors
Abstract
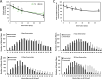
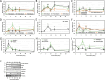
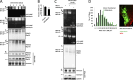
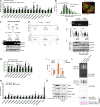
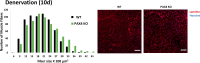
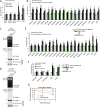
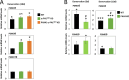
Proteasome activity is crucial for cellular integrity, but how tissues adjust proteasome content in response to catabolic stimuli is uncertain. Here, we demonstrate that transcriptional coordination by multiple transcription factors is required to increase proteasome content and activate proteolysis in catabolic states. Using denervated mouse muscle as a model system for accelerated proteolysis in vivo, we reveal that a two-phase transcriptional program activates genes encoding proteasome subunits and assembly chaperones to boost an increase in proteasome content. Initially, gene induction is necessary to maintain basal proteasome levels, and in a more delayed phase (7-10 days after denervation), it stimulates proteasome assembly to meet cellular demand for excessive proteolysis. Intriguingly, the transcription factors PAX4 and α-PALNRF-1 control the expression of proteasome among other genes in a combinatorial manner, driving cellular adaptation to muscle denervation. Consequently, PAX4 and α-PALNRF-1 represent new therapeutic targets to inhibit proteolysis in catabolic diseases (e.g., type-2 diabetes, cancer).
© 2024 Gilda et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures

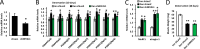

Update of
-
Proteasome gene expression is controlled by the coordinated functions of multiple transcription factors.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 4:2023.04.12.536627. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.12.536627. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Cell Biol. 2024 Aug 5;223(8):e202402046. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202402046. PMID: 37205440 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Proteasome gene expression is controlled by the coordinated functions of multiple transcription factors.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 4:2023.04.12.536627. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.12.536627. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Cell Biol. 2024 Aug 5;223(8):e202402046. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202402046. PMID: 37205440 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Coordinated regulation of protein synthesis and degradation by mTORC1.Nature. 2014 Sep 18;513(7518):440-3. doi: 10.1038/nature13492. Epub 2014 Jul 13. Nature. 2014. PMID: 25043031 Free PMC article.
-
Myofibril breakdown during atrophy is a delayed response requiring the transcription factor PAX4 and desmin depolymerization.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Feb 21;114(8):E1375-E1384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1612988114. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28096335 Free PMC article.
-
ER-Resident Transcription Factor Nrf1 Regulates Proteasome Expression and Beyond.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 23;21(10):3683. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103683. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32456207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of the 26S proteasome by Nrf1.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2018;94(8):325-336. doi: 10.2183/pjab.94.021. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30305478 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

