Long-term impact of familismo and ethnic identity on latinx college student drinking and high-risk consequences
- PMID: 38768079
- PMCID: PMC11106522
- DOI: 10.1080/15332640.2022.2082618
Long-term impact of familismo and ethnic identity on latinx college student drinking and high-risk consequences
Abstract
Familismo, ethnic pride, and ethnic shame were examined as longitudinal predictors of Latinx college student alcohol use and high-risk alcohol-related consequences. Latinx students completed measures during the fall of their first (T1), second (T2), and fourth (T4) year of college. T1 familismo was positively associated with T2 ethnic pride and negatively associated with T2 ethnic shame. T2 ethnic pride was negatively associated with T4 drinking, while T2 ethnic shame was positively associated with T4 drinking. T4 drinking was positively associated with T4 consequences. Results suggest that Latinx ethnic pride and ethnic shame during the second-year of college act as mediators between first-year familismo and fourth-year drinking and consequences.
Keywords: Latinx; alcohol; alcohol consequences; college; ethnic identity; familismo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
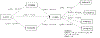
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th Author; Washington, DC.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
