Development of Novel Phosphonodifluoromethyl-Containing Phosphotyrosine Mimetics and a First-In-Class, Potent, Selective, and Bioavailable Inhibitor of Human CDC14 Phosphatases
- PMID: 38768084
- PMCID: PMC11764038
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00149
Development of Novel Phosphonodifluoromethyl-Containing Phosphotyrosine Mimetics and a First-In-Class, Potent, Selective, and Bioavailable Inhibitor of Human CDC14 Phosphatases
Abstract
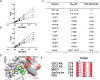
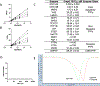
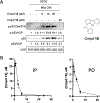
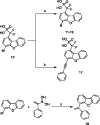
Together with protein tyrosine kinases, protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) control protein tyrosine phosphorylation and regulate numerous cellular functions. Dysregulated PTP activity is associated with the onset of multiple human diseases. Nevertheless, understanding of the physiological function and disease biology of most PTPs remains limited, largely due to the lack of PTP-specific chemical probes. In this study, starting from a well-known nonhydrolyzable phosphotyrosine (pTyr) mimetic, phosphonodifluoromethyl phenylalanine (F2Pmp), we synthesized 7 novel phosphonodifluoromethyl-containing bicyclic/tricyclic aryl derivatives with improved cell permeability and potency toward various PTPs. Furthermore, with fragment- and structure-based design strategies, we advanced compound 9 to compound 15, a first-in-class, potent, selective, and bioavailable inhibitor of human CDC14A and B phosphatases. This study demonstrates the applicability of the fragment-based design strategy in creating potent, selective, and bioavailable PTP inhibitors and provides a valuable probe for interrogating the biological roles of hCDC14 phosphatases and assessing their potential for therapeutic interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

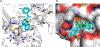
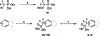
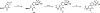
References
-
- Dodd GT; Xirouchaki CE; Eramo M; Mitchell CA; Andrews ZB; Henry BA; Cowley MA; Tiganis T Intranasal Targeting of Hypothalamic PTP1B and TCPTP Reinstates Leptin and Insulin Sensitivity and Promotes Weight Loss in Obesity. Cell Reports 2019, 28 (11), 2905–2922.e5. 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.08.019. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Manguso RT; Pope HW; Zimmer MD; Brown FD; Yates KB; Miller BC; Collins NB; Bi K; LaFleur MW; Juneja VR; Weiss SA; Lo J; Fisher DE; Miao D; Van Allen E; Root DE; Sharpe AH; Doench JG; Haining WN In Vivo CRISPR Screening Identifies Ptpn2 as a Cancer Immunotherapy Target. Nature 2017, 547 (7664), 413–418. 10.1038/nature23270. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

