Pilot robotic mastectomy in Singapore (PRoMiSing I) study: first safety and feasibility prospective cohort trial in South East Asia
- PMID: 38768466
- PMCID: PMC11392143
- DOI: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001674
Pilot robotic mastectomy in Singapore (PRoMiSing I) study: first safety and feasibility prospective cohort trial in South East Asia
Abstract
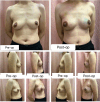
Background: Robotic mastectomy has been performed worldwide since 2015. The advantages of the robotic approach in nipple-sparing mastectomy have been proven with better visualization and preservation of blood supply to the nipple-areolar complex, with a lower incidence of necrosis. It also allows smaller incisions for both mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction. To date, no centers in Singapore and Southeast Asia offer robotic mastectomy. We believe that robotic mastectomy is a feasible and safe technique that our population can utilize.
Objectives: This study aimed to ascertain the surgical outcomes and perform a learning curve analysis in patients undergoing robotic mastectomy in a multi-ethnic South East Asian population.
Methods: A single-arm prospective pilot study of eligible patients aged 21-70 years old with early breast cancer or high-risk patients indicated for risk-reducing mastectomy who were eligible and consented to robotic mastectomy were enrolled in this trial from December 22, 2022 to December 15, 2023.
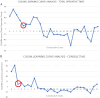
Results: A total of 29 consecutive robotic mastectomies were performed. The mean total operative time was 95±10.2 min. The average blood loss was 5.7±1.9 ml, and the average length of stay was 1.05 days. The mean mastectomy specimen weight was 251 g, and there was no conversion to conventional mastectomy in any case. Furthermore, there were no 30-day morbidity or complications in terms of wound infection requiring intervention, flap, and nipple-areolar complex necrosis, and postoperative hematoma/bleeding requiring intervention.
Conclusion: This study contributes to the current evidence that robotic mastectomy is a safe and feasible option and could prove to be a great alternative to conventional mastectomy. Further prospective trials examining the long-term oncological outcomes of robotic mastectomy will be performed to establish the oncologic safety of this technique in breast cancer treatment.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Postoperative complications and surgical outcomes of robotic versus conventional nipple-sparing mastectomy in breast cancer: meta-analysis.Br J Surg. 2024 Jan 3;111(1):znad336. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znad336. Br J Surg. 2024. PMID: 37890072 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy for the treatment of breast cancer: Feasibility and safety study.Breast. 2017 Feb;31:51-56. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2016.10.009. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Breast. 2017. PMID: 27810700 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer robotic nipple sparing mastectomy: evaluation of several surgical procedures and learning curve.World J Surg Oncol. 2019 Feb 6;17(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12957-019-1567-y. World J Surg Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30728011 Free PMC article.
-
Mastectomy with Reconstruction Including Robotic Endoscopic Surgery (MARRES): a prospective cohort study of the Korea Robot-Endoscopy Minimal Access Breast Surgery Study Group (KoREa-BSG) and Korean Breast Cancer Study Group (KBCSG).BMC Cancer. 2023 Jun 21;23(1):571. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10978-0. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37344780 Free PMC article.
-
Postoperative outcomes of minimally invasive versus conventional nipple-sparing mastectomy with prosthesis breast reconstruction in breast cancer: a meta-analysis.J Robot Surg. 2024 Jun 29;18(1):274. doi: 10.1007/s11701-024-02030-5. J Robot Surg. 2024. PMID: 38951387 Review.
Cited by
-
Consensus Statement on Robotic Nipple Sparing Mastectomy Expert Panel.J Breast Cancer. 2025 Jun;28(3):180-192. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2025.0030. Epub 2025 May 12. J Breast Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40432351 Free PMC article.
-
Organoid-Like Neurovascular Spheroids Promote the Recovery of Hypoxic-Ischemic Skin Flaps Through the Activation of Autophagy.Adv Healthc Mater. 2025 Jun;14(15):e2405154. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202405154. Epub 2025 Apr 16. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025. PMID: 40237031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lai HW, Chen ST, Tai CM, et al. . Robotic- versus endoscopic-assisted nipple-sparing mastectomy with immediate prosthesis breast reconstruction in the management of breast cancer: a case–control comparison study with analysis of clinical outcomes, learning curve, patient-reported aesthetic results, and medical cost. Ann Surg Oncol 2020;27:2255–2268. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical