Design of a targeted dual drug delivery system for boosting the efficacy of photoimmunotherapy against melanoma proliferation and metastasis
- PMID: 38768811
- PMCID: PMC12126733
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.05.017
Design of a targeted dual drug delivery system for boosting the efficacy of photoimmunotherapy against melanoma proliferation and metastasis
Abstract
Introduction: The combination of a photosensitizer and indoleamine-2,3 dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitor provides a promising photoimmunotherapy (PIT) strategy for melanoma treatment. A dual drug delivery system offers a potential approach for optimizing the inhibitory effects of PIT on melanoma proliferation and metastasis.
Objective: To develop a dual drug delivery system based on PIT and to study its efficacy in inhibiting melanoma proliferation and metastasis.
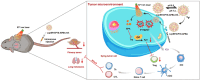
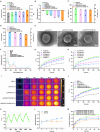
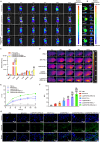
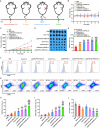
Methods: We constructed a multifunctional nano-porphyrin material (P18-APBA-HA) using the photosensitizer-purpurin 18 (P18), hyaluronic acid (HA), and 4-(aminomethyl) phenylboronic acid (APBA). The resulting P18-APBA-HA was inserted into a phospholipid membrane and the IDO inhibitor epacadostat (EPA) was loaded into the internal phase to prepare a dual drug delivery system (Lip\EPA\P18-APBA-HA). Moreover, we also investigated its physicochemical properties, targeting, anti-tumor immunity, and anti-tumor proliferation and metastasis effects.
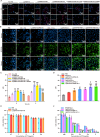
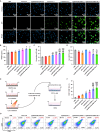
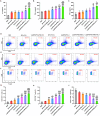
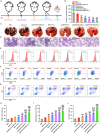
Results: The designed system utilized the pH sensitivity of borate ester to realize an enhanced-targeting strategy to facilitate the drug distribution in tumor lesions and efficient receptor-mediated cellular endocytosis. The intracellular release of EPA from Lip\EPA\P18-APBA-HA was triggered by thermal radiation, thereby inhibiting IDO activity in the tumor microenvironment, and promoting activation of the immune response. Intravenous administration of Lip\EPA\P18-APBA-HA effectively induced anti-tumor immunity by promoting dendritic cell maturation, cytotoxic T cell activation, and regulatory T cell suppression, and regulating cytokine secretion, to inhibit the proliferation of melanoma and lung metastasis.
Conclusion: The proposed nano-drug delivery system holds promise as offers a promising strategy to enhance the inhibitory effects of the combination of EPA and P18 on melanoma proliferation and metastasis.
Keywords: 3 dioxygenase inhibitor; Indoleamine-2; Melanoma; Photoimmunotherapy; Purpurin 18; pH-triggered delivery.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel NIR-dependent IDO-inhibiting ethosomes treatment melanoma through PTT/PDT/immunotherapy synergy.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2025 Jul;251:114565. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2025.114565. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2025. PMID: 39999696
-
Cold to Hot: Binary Cooperative Microneedle Array-Amplified Photoimmunotherapy for Eliciting Antitumor Immunity and the Abscopal Effect.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Jul 22;12(29):32259-32269. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c05090. Epub 2020 May 22. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32406239
-
A Porphyrin Nanomaterial for Photoimmunotherapy for Treatment of Melanoma.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jun;12(21):e2414592. doi: 10.1002/advs.202414592. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40202119 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic acid-modified liposomal honokiol nanocarrier: Enhance anti-metastasis and antitumor efficacy against breast cancer.Carbohydr Polym. 2020 May 1;235:115981. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115981. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Carbohydr Polym. 2020. PMID: 32122511 Review.
-
Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy of Cancer.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Aug 20;52(8):2332-2339. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00273. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31335117 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems for Enhanced Melanoma Immunotherapy.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Aug 7;19:6789-6816. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S517331. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40792218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Approach for Bladder Cancer Treatment: Nanoparticles as a Drug Delivery System.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Dec 17;19:13461-13483. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S498729. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39713223 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zou J., Li L., Yang Z., Chen X. Phototherapy meets immunotherapy: a win–win strategy to fight against cancer. Nanophotonics. 2021;10:3229. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2021-0209. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

