Hypomethylation-enhanced CRTC2 expression drives malignant phenotypes and primary resistance to immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38770131
- PMCID: PMC11103543
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109821
Hypomethylation-enhanced CRTC2 expression drives malignant phenotypes and primary resistance to immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
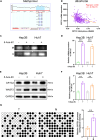
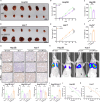
The cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB)-regulated transcription coactivator 2 (CRTC2) is a crucial regulator of hepatic lipid metabolism and gluconeogenesis and correlates with tumorigenesis. However, the mechanism through which CRTC2 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression is largely unknown. Here, we found that increased CRTC2 expression predicted advanced tumor grade and stage, as well as worse prognosis in patients with HCC. DNA promoter hypomethylation led to higher CRTC2 expression in HCC. Functionally, CRTC2 contributed to HCC malignant phenotypes through the activated Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which could be abrogated by the small-molecular inhibitor XAV-939. Moreover, Crtc2 facilitated tumor growth while concurrently downregulating the PD-L1/PD-1 axis, resulting in primary resistance to immunotherapy. In immunocompetent mice models of HCC, targeting Crtc2 in combination with anti-PD-1 therapy prominently suppressed tumor growth by synergistically enhancing responsiveness to immunotherapy. Collectively, targeting CRTC2 might be a promising therapeutic strategy to sensitize immunotherapy in HCC.
Keywords: Cancer; Immunology; Molecular biology.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The SMILE transcriptional corepressor inhibits cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)-mediated transactivation of gluconeogenic genes.J Biol Chem. 2018 Aug 24;293(34):13125-13133. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002196. Epub 2018 Jun 27. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29950523 Free PMC article.
-
CREB-upregulated lncRNA MEG3 promotes hepatic gluconeogenesis by regulating miR-302a-3p-CRTC2 axis.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Mar;120(3):4192-4202. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27706. Epub 2018 Sep 27. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30260029
-
AMPK-dependent repression of hepatic gluconeogenesis via disruption of CREB.CRTC2 complex by orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 15;285(42):32182-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.134890. Epub 2010 Aug 5. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20688914 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CRTC2 in Metabolic Homeostasis: Key Regulator of Whole-Body Energy Metabolism?Diabetes Metab J. 2020 Aug;44(4):498-508. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0200. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Diabetes Metab J. 2020. PMID: 32174060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological functions of CRTC2 and its role in metabolism-related diseases.J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep;17(3):495-506. doi: 10.1007/s12079-023-00730-5. Epub 2023 Mar 1. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36856929 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive review and updated analysis of DNA methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma: From basic research to clinical application.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Nov;14(11):e70066. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70066. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39462685 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li Q., Ni Y., Zhang L., Jiang R., Xu J., Yang H., Hu Y., Qiu J., Pu L., Tang J., Wang X. HIF-1alpha-induced expression of m6A reader YTHDF1 drives hypoxia-induced autophagy and malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting ATG2A and ATG14 translation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021;6:76. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00453-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

