Before Translating Extracellular Vesicles into Personalized Diagnostics and Therapeutics: What We Could Do
- PMID: 38771015
- PMCID: PMC11151200
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.4c00185
Before Translating Extracellular Vesicles into Personalized Diagnostics and Therapeutics: What We Could Do
Abstract
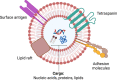
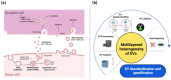
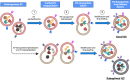
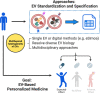
Extracellular vesicle (EV) research is rapidly advancing from fundamental science to translational applications in EV-based personalized therapeutics and diagnostics. Yet, fundamental questions persist regarding EV biology and mechanisms, particularly concerning the heterogeneous interactions between EVs and cells. While we have made strides in understanding virus delivery and intracellular vesicle transport, our comprehension of EV trafficking remains limited. EVs are believed to mediate intercellular communication through cargo transfer, but uncertainties persist regarding the occurrence and quantification of EV-cargo delivery within acceptor cells. This ambiguity is crucial to address, given the significant translational impact of EVs on therapeutics and diagnostics. This perspective article does not seek to provide exhaustive recommendations and guidance on EV-related studies, as these are well-articulated in position papers and statements by the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles (ISEV), including the 'Minimum Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles' (MISEV) 2014, MISEV2018, and the recent MISEV2023. Instead, recognizing the multilayered heterogeneity of EVs as both a challenge and an opportunity, this perspective emphasizes novel approaches to facilitate our understanding of diverse EV biology, address uncertainties, and leverage this knowledge to advance EV-based personalized diagnostics and therapeutics. Specifically, this perspective synthesizes current insights, identifies opportunities, and highlights exciting technological advancements in ultrasensitive single EV or "digital" profiling developed within the author's multidisciplinary group. These newly developed technologies address technical gaps in dissecting the molecular contents of EV subsets, contributing to the evolution of EVs as next-generation liquid biopsies for diagnostics and providing better quality control for EV-based therapeutics.
Keywords: diagnostics; drug delivery; exosome; extracellular vesicle; personalized medicine; protein biomarker; single molecule array.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles, RNA sequencing, and bioinformatic analyses: Challenges, solutions, and recommendations.J Extracell Vesicles. 2024 Dec;13(12):e70005. doi: 10.1002/jev2.70005. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024. PMID: 39625409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative analysis of the minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles guidelines: Advancements and implications for extracellular vesicle research.Semin Cancer Biol. 2024 Jun;101:12-24. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2024.04.002. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Semin Cancer Biol. 2024. PMID: 38657746 Review.
-
Toward Clarity in Single Extracellular Vesicle Research: Defining the Field and Correcting Missteps.ACS Nano. 2025 May 6;19(17):16193-16203. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5c00705. Epub 2025 Apr 24. ACS Nano. 2025. PMID: 40271998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenesis, Membrane Trafficking, Functions, and Next Generation Nanotherapeutics Medicine of Extracellular Vesicles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 May 18;16:3357-3383. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S310357. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34040369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles (MISEV): Ten-Year Evolution (2014-2023).Pharmaceutics. 2024 Oct 29;16(11):1394. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16111394. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39598518 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosome isolation and characterization for advanced diagnostic and therapeutic applications.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Feb 25;31:101613. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101613. eCollection 2025 Apr. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40161926 Free PMC article.
-
Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Cord Blood Plasma and Placental Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Acute Lung Injury Induced by Lipopolysaccharide (LPS).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 25;26(1):75. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010075. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39795932 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles as vital players in drug delivery: a focus on clinical disease treatment.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 May 14;13:1600227. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1600227. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40438295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles: their challenges and benefits as potential biomarkers for musculoskeletal disorders.J Int Med Res. 2025 Feb;53(2):3000605251317476. doi: 10.1177/03000605251317476. J Int Med Res. 2025. PMID: 39973226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stoichiometric constraints for detection of EV-borne biomarkers in blood.J Extracell Vesicles. 2025 Feb;14(2):e70034. doi: 10.1002/jev2.70034. J Extracell Vesicles. 2025. PMID: 39901737 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Welsh J. A.; Goberdhan D. C. I.; O’Driscoll L.; Buzas E. I.; Blenkiron C.; Bussolati B.; Cai H.; Di Vizio D.; Driedonks T. A. P.; Erdbrügger U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13 (2), e12404.10.1002/jev2.12404. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pegtel D. M.; Cosmopoulos K.; Thorley-Lawson D. A.; van Eijndhoven M. A.; Hopmans E. S.; Lindenberg J. L.; de Gruijl T. D.; Würdinger T.; Middeldorp J. M. Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2010, 107 (14), 6328–6333. 10.1073/pnas.0914843107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

