lncRNA CDKN2B-AS1 is downregulated in patients with ventricular fibrillation in acute myocardial infarction
- PMID: 38771854
- PMCID: PMC11108170
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304041
lncRNA CDKN2B-AS1 is downregulated in patients with ventricular fibrillation in acute myocardial infarction
Abstract
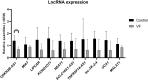
Ventricular fibrillation (VF) in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is the main cause of deaths occurring in the acute phase of an ischemic event. Although it is known that genetics may play an important role in this pathology, the possible role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNA) has never been studied. Therefore, the aim of this work is to study the expression of 10 lncRNAs in patients with and without VF in AMI. For this purpose, the expression of CDKN2B-AS1, KCNQ1OT1, LIPCAR, MALAT1, MIAT, NEAT1, SLC16A1-AS1, lnc-TK2-4:2, TNFRSF14-AS1, and UCA1 were analyzed. After the analysis and Bonferroni correction, the lncRNA CDKN2B-AS showed a statistical significance lower expression (P values of 2.514 x 10-5). In silico analysis revealed that six proteins could be related to the possible effect of lncRNA CDKN2B-AS1: AGO3, PLD4, POU4F1, ZNF26, ZNF326 and ZNF431. These in silico proteins predicted to have a low cardiac expression, although there is no literature indicating a potential relationship with VF in AMI. Thus, the lncRNA CDKN2B-AS1 shows a significant lower expression in patients with VF in AMI vs patients without VF in AMI. Literature data suggest that the role of CDKN2B1-AS is related to the miR-181a/SIRT1 pathway.
Copyright: © 2024 Pan-Lizcano et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA muscleblind like splicing regulator 1 antisense RNA 1 (LncRNA MBNL1-AS1) promotes the progression of acute myocardial infarction by regulating the microRNA-132-3p/SRY-related high-mobility-group box 4 (SOX4) axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Jan;13(1):1424-1435. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2018974. Bioengineered. 2022. Retraction in: Bioengineered. 2024 Dec;15(1):2299561. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2024.2299561. PMID: 34978261 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
LncRNA SLC8A1-AS1 protects against myocardial damage through activation of cGMP-PKG signaling pathway by inhibiting SLC8A1 in mice models of myocardial infarction.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):9019-9032. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27574. Epub 2018 Oct 30. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30378115
-
CDKN2B-AS1 is overexpressed in polycystic ovary syndrome and sponges miR-181a to promote granulosa cell proliferation.Anticancer Drugs. 2023 Feb 1;34(2):207-213. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001405. Epub 2023 Oct 24. Anticancer Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36622742 Free PMC article.
-
Research advances on circulating long noncoding RNAs as biomarkers of cardiovascular diseases.Int J Cardiol. 2022 Apr 15;353:109-117. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2022.01.070. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Int J Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35143876 Review.
-
CDKN2B-AS1: An Indispensable Long Non-coding RNA in Multiple Diseases.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(41):5335-5346. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200806102424. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 32767927
References
-
- Weizman O, Marijon E, Narayanan K, Boveda S, Defaye P, Martins R, et al.. Incidence, Characteristics, and Outcomes of Ventricular Fibrillation Complicating Acute Myocardial Infarction in Women Admitted Alive in the Hospital. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2022;11: e025959. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.025959 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials