The evolution of sex roles: The importance of ecology and social environment
- PMID: 38771872
- PMCID: PMC11145285
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2321294121
The evolution of sex roles: The importance of ecology and social environment
Abstract
Males and females often have different roles in reproduction, although the origin of these differences has remained controversial. Explaining the enigmatic reversed sex roles where males sacrifice their mating potential and provide full parental care is a particularly long-standing challenge in evolutionary biology. While most studies focused on ecological factors as the drivers of sex roles, recent research highlights the significance of social factors such as the adult sex ratio. To disentangle these propositions, here, we investigate the additive and interactive effects of several ecological and social factors on sex role variation using shorebirds (sandpipers, plovers, and allies) as model organisms that provide the full spectrum of sex role variation including some of the best-known examples of sex-role reversal. Our results consistently show that social factors play a prominent role in driving sex roles. Importantly, we show that reversed sex roles are associated with both male-skewed adult sex ratios and high breeding densities. Furthermore, phylogenetic path analyses provide general support for sex ratios driving sex role variations rather than being a consequence of sex roles. Together, these important results open future research directions by showing that different mating opportunities of males and females play a major role in generating the evolutionary diversity of sex roles, mating system, and parental care.
Keywords: adult sex ratio; habitat productivity; mating system; parental care; sex-role reversal.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
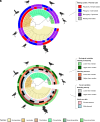

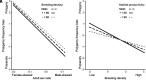
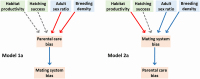
References
-
- Davies N. B., Krebs J. R., West S. A., An Introduction to Behavioural Ecology (Wiley-Blackwell, ed. 4, 2013).
-
- Alcock J., Animal Behavior: An Evolutionary Approach (Sinauer Associates, Inc, ed. 10, 2013).
-
- Székely T., et al. , The causes and implications of sex role diversity in shorebird breeding systems. Ibis 166, 357–385 (2023) 10.1111/ibi.13277. - DOI
-
- Herridge E. J., Murray R. L., Gwynne D. T., Bussière L. F., Mating and parental sex roles, diversity. Encycl. Evol. Biol. 2, 453–458 (2016).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- KH130430/Nemzeti Kutatási Fejlesztési és Innovációs Hivatal (NKFI)
- PD134414/Nemzeti Kutatási Fejlesztési és Innovációs Hivatal (NKFI)
- ANN143995/Nemzeti Kutatási Fejlesztési és Innovációs Hivatal (NKFI)
- ÉLVONAL KKP-126949/Nemzeti Kutatási Fejlesztési és Innovációs Hivatal (NKFI)
- K-116310/Nemzeti Kutatási Fejlesztési és Innovációs Hivatal (NKFI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

