Sex differences in the structure and function of the vasopressin system in the ventral pallidum are associated with the sex-specific regulation of social play behavior in juvenile rats
- PMID: 38772158
- PMCID: PMC11221216
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2024.105563
Sex differences in the structure and function of the vasopressin system in the ventral pallidum are associated with the sex-specific regulation of social play behavior in juvenile rats
Abstract
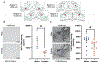
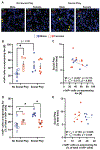
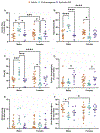
Vasopressin (AVP) regulates various social behaviors, often in sex-specific ways, including social play behavior, a rewarding behavior displayed primarily by juveniles. Here, we examined whether and how AVP acting in the brain's reward system regulates social play behavior in juvenile rats. Specifically, we focused on AVP signaling in the ventral pallidum (VP), a brain region that is a part of the reward system. First, we examined the organization of the VP-AVP system in juvenile rats and found sex differences, with higher density of both AVP-immunoreactive fibers and AVP V1a receptor (V1aR) binding in males compared to females while females show a greater number of V1aR-expressing cells compared to males. We further found that, in both sexes, V1aR-expressing cells co-express a GABA marker to a much greater extent (approx. 10 times) than a marker for glutamate. Next, we examined the functional involvement of V1aR-expressing VP cells in social play behavior. We found that exposure to social play enhanced the proportion of activated V1aR-expressing VP cells in males only. Finally, we showed that infusion of a specific V1aR antagonist into the VP increased social play behaviors in juvenile male rats while decreasing these behaviors in juvenile female rats. Overall, these findings reveal structural and functional sex differences in the AVP-V1aR system in the VP that are associated with the sex-specific regulation of social play behavior.
Keywords: Juvenile rats; Sex differences; Social play behavior; Vasopressin.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Vasopressin regulates social play behavior in sex-specific ways through glutamate modulation in the lateral septum.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025 Mar;50(4):630-639. doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-01987-z. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39304743
-
Sex difference in the effects of ventral pallidum vasopressin 1a receptor partial knockdown on social behavior in mice.Horm Behav. 2025 Aug;174:105792. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2025.105792. Epub 2025 Jul 26. Horm Behav. 2025. PMID: 40716389
-
Involvement of ventral pallidal vasopressin in the sex-specific regulation of sociosexual motivation in rats.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2020 Jan;111:104462. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2019.104462. Epub 2019 Sep 25. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2020. PMID: 31586844 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of environmental toxicant exposures on oxytocin and vasopressin systems in the developing brain: factors imparting risk and resilience.Behav Brain Res. 2025 Oct 2;494:115723. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2025.115723. Epub 2025 Jul 3. Behav Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 40617300 Review.
-
Arginine vasopressin in mood disorders: A potential biomarker of disease pathology and a target for pharmacologic intervention.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024 Sep;78(9):495-506. doi: 10.1111/pcn.13703. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38923665 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
To Play or Not to Play? Effects of Playmate Familiarity and Social Isolation on Social Play Engagement in Three Laboratory Rat Strains.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 15:2024.11.14.623692. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.14.623692. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Physiol Behav. 2025 Sep 2;302:115080. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2025.115080. PMID: 39605718 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Ventral pallidal regulation of motivated behaviors and reinforcement.Front Neural Circuits. 2023 Feb 2;17:1086053. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2023.1086053. eCollection 2023. Front Neural Circuits. 2023. PMID: 36817646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The transcriptome of playfulness is sex biased in the juvenile rat medial amygdala: A role for inhibitory neurons.Cell Rep. 2025 Jun 24;44(6):115782. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115782. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40478737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bekoff M (1974) Social Play and Play-Soliciting by Infant Canids. Am Zool 14:323–340.
-
- Ben-Yishay R, Shav-Tal Y (2019) The dynamic lifecycle of mRNA in the nucleus. Curr Opin Cell Biol 58:69–75. - PubMed
-
- Bosch OJ, Pförtsch J, Beiderbeck DI, Landgraf R, Neumann ID (2010) Maternal behaviour is associated with vasopressin release in the medial preoptic area and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the rat. J Neuroendocrinol 22:420–429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

