In vivo neutralization of coral snake venoms with an oligoclonal nanobody mixture in a murine challenge model
- PMID: 38773068
- PMCID: PMC11109316
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-48539-z
In vivo neutralization of coral snake venoms with an oligoclonal nanobody mixture in a murine challenge model
Abstract
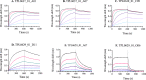
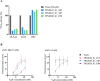
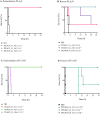
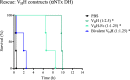
Oligoclonal mixtures of broadly-neutralizing antibodies can neutralize complex compositions of similar and dissimilar antigens, making them versatile tools for the treatment of e.g., infectious diseases and animal envenomations. However, these biotherapeutics are complicated to develop due to their complex nature. In this work, we describe the application of various strategies for the discovery of cross-neutralizing nanobodies against key toxins in coral snake venoms using phage display technology. We prepare two oligoclonal mixtures of nanobodies and demonstrate their ability to neutralize the lethality induced by two North American coral snake venoms in mice, while individual nanobodies fail to do so. We thus show that an oligoclonal mixture of nanobodies can neutralize the lethality of venoms where the clinical syndrome is caused by more than one toxin family in a murine challenge model. The approaches described may find utility for the development of advanced biotherapeutics against snakebite envenomation and other pathologies where multi-epitope targeting is beneficial.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests: M.B.V., A.L., and A.H.L. are inventors on a submitted patent application (EP23192644.5), owned by the Technical University of Denmark. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phage display-derived alpaca nanobodies as potential therapeutics for Naja atra snake envenomation.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Aug 21;90(8):e0012124. doi: 10.1128/aem.00121-24. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38980046 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological cross-recognition and neutralization studies of Micrurus mipartitus and Micrurus dumerilii venoms by two therapeutic equine antivenoms.Biologicals. 2020 Nov;68:40-45. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2020.08.011. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Biologicals. 2020. PMID: 32928631
-
A Simple and Novel Strategy for the Production of a Pan-specific Antiserum against Elapid Snakes of Asia.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Apr 8;10(4):e0004565. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004565. eCollection 2016 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 27058956 Free PMC article.
-
Snake antivenom: Challenges and alternate approaches.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Nov;181:114135. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114135. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32628928 Review.
-
Coral snake bites (Micrurus spp.) in Brazil: a review of literature reports.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016 Mar;54(3):222-34. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2015.1135337. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016. PMID: 26808120 Review.
Cited by
-
Next-generation snakebite therapies could reduce death toll.Nature. 2024 Nov 21. doi: 10.1038/d41586-024-03818-z. Online ahead of print. Nature. 2024. PMID: 39572669 No abstract available.
-
Importance of the Cysteine-Rich Domain of Snake Venom Prothrombin Activators: Insights Gained from Synthetic Neutralizing Antibodies.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Aug 15;16(8):361. doi: 10.3390/toxins16080361. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39195771 Free PMC article.
-
Microbes Saving Lives and Reducing Suffering.Microb Biotechnol. 2025 Jan;18(1):e70068. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.70068. Microb Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39844583 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Discovery of broadly neutralizing VHHs against short-chain α-neurotoxins using a consensus toxin as an antigen.MAbs. 2025 Dec;17(1):2522838. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2025.2522838. Epub 2025 Jun 28. MAbs. 2025. PMID: 40581770 Free PMC article.
-
Target product profiles for pan-Africa recombinant antivenoms against neurotoxic or hemotoxic and cytotoxic snakebite envenoming.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025 Jan 24;19(1):e0012833. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012833. eCollection 2025 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025. PMID: 39854596 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 221702/Z/20/Z/Wellcome Trust (Wellcome)
- 00025302/Villum Fonden (Villum Foundation)
- 713683/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 850974/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 899987/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

