Stacked neural network for predicting polygenic risk score
- PMID: 38773257
- PMCID: PMC11109142
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-62513-1
Stacked neural network for predicting polygenic risk score
Abstract
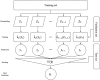
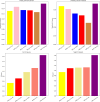
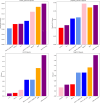
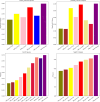
In recent years, the utility of polygenic risk scores (PRS) in forecasting disease susceptibility from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) results has been widely recognised. Yet, these models face limitations due to overfitting and the potential overestimation of effect sizes in correlated variants. To surmount these obstacles, we devised the Stacked Neural Network Polygenic Risk Score (SNPRS). This novel approach synthesises outputs from multiple neural network models, each calibrated using genetic variants chosen based on diverse p-value thresholds. By doing so, SNPRS captures a broader array of genetic variants, enabling a more nuanced interpretation of the combined effects of these variants. We assessed the efficacy of SNPRS using the UK Biobank data, focusing on the genetic risks associated with breast and prostate cancers, as well as quantitative traits like height and BMI. We also extended our analysis to the Korea Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) dataset. Impressively, our results indicate that SNPRS surpasses traditional PRS models and an isolated deep neural network in terms of accuracy, highlighting its promise in refining the efficacy and relevance of PRS in genetic studies.
Keywords: Deep learning; Ensemble learning; Polygenic risk score.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polygenic risk scores for the prediction of common cancers in East Asians: A population-based prospective cohort study.Elife. 2023 Mar 27;12:e82608. doi: 10.7554/eLife.82608. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36971353 Free PMC article.
-
Benchmarking multi-ancestry prostate cancer polygenic risk scores in a real-world cohort.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 Apr 10;20(4):e1011990. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011990. eCollection 2024 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 38598551 Free PMC article.
-
Deep neural network improves the estimation of polygenic risk scores for breast cancer.J Hum Genet. 2021 Apr;66(4):359-369. doi: 10.1038/s10038-020-00832-7. Epub 2020 Oct 2. J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33009504
-
Polygenic risk score for genetic evaluation of prostate cancer risk in Asian populations: A narrative review.Investig Clin Urol. 2021 May;62(3):256-266. doi: 10.4111/icu.20210124. Investig Clin Urol. 2021. PMID: 33943048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide association studies and polygenic risk scores for skin cancer: clinically useful yet?Br J Dermatol. 2019 Dec;181(6):1146-1155. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17917. Epub 2019 Jul 7. Br J Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30908599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide association neural networks identify genes linked to family history of Alzheimer's disease.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Nov 22;26(1):bbae704. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae704. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39775791 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of deep-learning-based approaches to improve polygenic scores.Nat Commun. 2025 Jun 2;16(1):5122. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60056-1. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40456720 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

