MR-based radiomics predictive modelling of EGFR mutation and HER2 overexpression in metastatic brain adenocarcinoma: a two-centre study
- PMID: 38773634
- PMCID: PMC11110398
- DOI: 10.1186/s40644-024-00709-4
MR-based radiomics predictive modelling of EGFR mutation and HER2 overexpression in metastatic brain adenocarcinoma: a two-centre study
Abstract
Objectives: Magnetic resonance (MR)-based radiomics features of brain metastases are utilised to predict epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpression in adenocarcinoma, with the aim to identify the most predictive MR sequence.
Methods: A retrospective inclusion of 268 individuals with brain metastases from adenocarcinoma across two institutions was conducted. Utilising T1-weighted imaging (T1 contrast-enhanced [T1-CE]) and T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (T2-FLAIR) sequences, 1,409 radiomics features were extracted. These sequences were randomly divided into training and test sets at a 7:3 ratio. The selection of relevant features was done using the least absolute shrinkage selection operator, and the training cohort's support vector classifier model was employed to generate the predictive model. The performance of the radiomics features was evaluated using a separate test set.
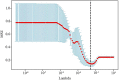
Results: For contrast-enhanced T1-CE cohorts, the radiomics features based on 19 selected characteristics exhibited excellent discrimination. No significant differences in age, sex, and time to metastasis were observed between the groups with EGFR mutations or HER2 + and those with wild-type EGFR or HER2 (p > 0.05). Radiomics feature analysis for T1-CE revealed an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.98, classification accuracy of 0.93, sensitivity of 0.92, and specificity of 0.93 in the training cohort. In the test set, the AUC was 0.82. The 19 radiomics features for the T2-FLAIR sequence showed AUCs of 0.86 in the training set and 0.70 in the test set.
Conclusions: This study developed a T1-CE signature that could serve as a non-invasive adjunctive tool to determine the presence of EGFR mutations and HER2 + status in adenocarcinoma, aiding in the direction of treatment plans.
Clinical relevance statement: We propose radiomics features based on T1-CE brain MR sequences that are both evidence-based and non-invasive. These can be employed to guide clinical treatment planning in patients with brain metastases from adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: Adenocarcinoma; Brain metastasis; Gene expression; Radiomics; T1-CE brain MR sequences.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Radiomics signature of brain metastasis: prediction of EGFR mutation status.Eur Radiol. 2021 Jul;31(7):4538-4547. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07614-x. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33439315
-
Deep learning radiomics for the prediction of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status based on MRI in brain metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma patients.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 12;25(1):443. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13823-8. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40075375 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiating EGFR from ALK mutation status using radiomics signature based on MR sequences of brain metastasis.Eur J Radiol. 2022 Oct;155:110499. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2022.110499. Epub 2022 Aug 27. Eur J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 36049410
-
Distinguishing EGFR mutation molecular subtypes based on MRI radiomics features of lung adenocarcinoma brain metastases.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2024 May;240:108258. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2024.108258. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2024. PMID: 38552362
-
A Bayesian meta-analysis on MRI-based radiomics for predicting EGFR mutation in brain metastasis of lung cancer.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Feb 10;25(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01566-8. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39930347 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The clinical implications and interpretability of computational medical imaging (radiomics) in brain tumors.Insights Imaging. 2025 Mar 30;16(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13244-025-01950-6. Insights Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40159380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated plasma HSP90α as a prognostic marker in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2025 Jul 22;30(4):457. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.15203. eCollection 2025 Oct. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40762018 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic, Therapeutic, and Prognostic Applications of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the Clinical Management of Brain Metastases (BMs).Brain Sci. 2025 Jul 8;15(7):730. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15070730. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40722321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroimaging insights into lung disease-related brain changes: from structure to function.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Feb 20;17:1550319. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1550319. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40051465 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

