Diagnosis of Arboleda-Tham syndrome by whole-exome sequencing in an Asian girl with severe developmental delay
- PMID: 38773911
- PMCID: PMC11109524
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.2420
Diagnosis of Arboleda-Tham syndrome by whole-exome sequencing in an Asian girl with severe developmental delay
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to report a severe phenotype of Arboleda-Tham syndrome in a 20-month-old girl, characterized by global developmental delay, distinct facial features, intellectual disability. Arboleda-Tham syndrome is known for its wide phenotypic spectrum and is associated with truncating variants in the KAT6A gene.
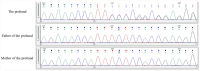
Methods: To diagnose this case, a combination of clinical phenotype assessment and whole-exome sequencing technology was employed. The genetic analysis involved whole-exome sequencing, followed by confirmation of the identified variant through Sanger sequencing.
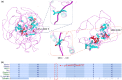
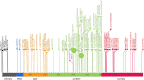
Results: The whole-exome sequencing revealed a novel de novo frameshift mutation c.3048del (p.Leu1017Serfs*17) in the KAT6A gene, which is classified as likely pathogenic. This mutation was not found in the ClinVar and HGMD databases and was not present in her parents. The mutation leads to protein truncation or activation of nonsense-mediated mRNA degradation. The mutation is located within exon 16, potentially leading to protein truncation or activation of nonsense-mediated mRNA degradation. Protein modeling suggested that the de novo KAT6A mutation might alter hydrogen bonding and reduce protein stability, potentially damaging the protein structure and function.
Conclusion: This study expands the understanding of the genetic basis of Arboleda-Tham syndrome, highlighting the importance of whole-exome sequencing in diagnosing cases with varied clinical presentations. The discovery of the novel KAT6A mutation adds to the spectrum of known pathogenic variants and underscores the significance of this gene in the syndrome's pathology.
Keywords: Arboleda‐Tham syndrome; KAT6A; de novo truncating variants; facial dysmorphism; global developmental delay.
© 2024 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive review and outline of genotypes and phenotypes of Arboleda-Tham syndrome spectrum: insights from novel variants.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Feb 18;52(1):242. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10302-y. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39964375 Review.
-
Fetal hepatic calcification in severe KAT6A (Arboleda-Tham) syndrome.Eur J Med Genet. 2024 Feb;67:104906. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2023.104906. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Eur J Med Genet. 2024. PMID: 38143025
-
Phenotypic variability in a family with an inherited KAT6A frameshift variant.Eur J Med Genet. 2025 Feb;73:104993. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2024.104993. Epub 2024 Dec 29. Eur J Med Genet. 2025. PMID: 39740728
-
A de novo heterozygous variant in KAT6A is associated with a newly named neurodevelopmental disorder Arboleda-Tham syndrome-a case report.Transl Pediatr. 2021 Jun;10(6):1748-1754. doi: 10.21037/tp-21-206. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34295791 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel KAT6A variant in an infant presenting with facial dysmorphism and developmental delay: a case report and literature review.BMC Med Genomics. 2021 Dec 20;14(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s12920-021-01148-x. BMC Med Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34930245 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical features and airway management experience in an infant with Arboleda-Tham syndrome.Can J Anaesth. 2025 Jun;72(6):1028-1029. doi: 10.1007/s12630-025-02966-8. Epub 2025 May 20. Can J Anaesth. 2025. PMID: 40394407 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ai, Q. , Jiang, L. , Chen, Y. , Yao, X. , Yin, J. , & Chen, S. (2023). A case of KAT6A syndrome with a newly discovered mutation in the KAT6A gene, mainly manifested as bone marrow failure syndrome. Hematology, 28(1), 2182159. - PubMed
-
- Arboleda, V. A. , Lee, H. , Dorrani, N. , Zadeh, N. , Willis, M. , Macmurdo, C. F. , Manning, M. A. , Kwan, A. , Hudgins, L. , Barthelemy, F. , Miceli, M. C. , Quintero‐Rivera, F. , Kantarci, S. , Strom, S. P. , Deignan, J. L. , UCLA Clinical Genomics Center , Grody, W. W. , Vilain, E. , & Nelson, S. F. (2015). De novo nonsense mutations in KAT6A, a lysine acetyl‐transferase gene, cause a syndrome including microcephaly and global developmental delay. American Journal of Human Genetics, 96(3), 498–506. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bukvic, N. , Chetta, M. , Bagnulo, R. , Leotta, V. , Pantaleo, A. , Palumbo, O. , Palumbo, P. , Oro, M. , Rivieccio, M. , Laforgia, N. , de Rinaldis, M. , Rosati, A. , Kerkhof, J. , Sadikovic, B. , & Resta, N. (2023, January 7). What have we learned from patients who have Arboleda‐Tham syndrome due to a De novo KAT6A pathogenic variant with impaired histone acetyltransferase function? A precise clinical description may Be critical for genetic testing approach and final diagnosis. Genes (Basel), 14(1), 165. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Champagne, N. , Pelletier, N. , & Yang, X. J. (2001). The monocytic leukemia zinc finger protein MOZ is a histone acetyltransferase. Oncogene, 20(3), 404–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

