Circulating MicroRNA as Biomarkers of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review
- PMID: 38774014
- PMCID: PMC11103047
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2023.12.009
Circulating MicroRNA as Biomarkers of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review
Abstract
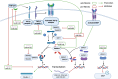
Close monitoring for cardiotoxicity during anthracycline chemotherapy is crucial for early diagnosis and therapy guidance. Currently, monitoring relies on cardiac imaging and serial measurement of cardiac biomarkers like cardiac troponin and natriuretic peptides. However, these conventional biomarkers are nonspecific indicators of cardiac damage. Exploring new, more specific biomarkers with a clear link to the underlying pathomechanism of cardiotoxicity holds promise for increased specificity and sensitivity in detecting early anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. miRNAs (microRNAs), small single-stranded, noncoding RNA sequences involved in epigenetic regulation, influence various physiological and pathological processes by targeting expression and translation. Emerging as new biomarker candidates, circulating miRNAs exhibit resistance to degradation and offer a direct pathomechanistic link. This review comprehensively outlines their potential as early biomarkers for cardiotoxicity and their pathomechanistic link.
Keywords: cardiomyopathy; cardiotoxicity; chemotherapy; circulating biomarkers; epigenetics; heart failure.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by the Flanders Research Foundation - FWO (research grant G055821N, doctoral research grant 1192420N to Dr Boen and senior clinical investigator grant 1804320N to Dr Van Craenenbroeck) and by the Belgian Foundation against Cancer (research grant C/2020/1374 and clinical mandate grant to CF 2021/1594). Ms Cherubin was an Early Stage Researcher fellow on the INSPIRE project, which has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program (H2020-MSCA-ITN program, Grant Agreement: No858070), and has received a SEP-grant from the Research Council of the University of Antwerp. Mr Bosman was supported as a predoctoral fellow by the Fund for Scientific Research (FWO) Flanders (grant number: 1S33720N). Dr Loeys holds a consolidator grant from the European Research Council (Genomia – ERC-COG-2017-771945). Dr Gevaert has received institutional lecture/advisory board fees from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, and Menarini outside the submitted work. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures
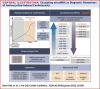
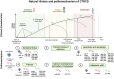
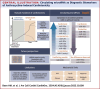
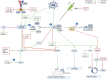
References
-
- Lyon A.R., López-Fernández T., Couch L.S., et al. 2022 ESC guidelines on cardio-oncology developed in collaboration with the European Hematology Association (EHA), the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ESTRO) and the International Cardio-Oncology Society (IC-OS) Eur Heart J. 2022;43(41):4229–4361. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac244. - DOI - PubMed
-
- López-Sendón J., Álvarez-Ortega C., Zamora Auñon P., et al. Classification, prevalence, and outcomes of anticancer therapy-induced cardiotoxicity: the CARDIOTOX registry. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:1720–1729. - PubMed
-
- Cardinale D., Colombo A., Bacchiani G., et al. Early detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy. Circulation. 2015;131:1981–1988. - PubMed
-
- Octavia Y., Tocchetti C.G., Gabrielson K.L., Janssens S., Crijns H.J., Moens A.L. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012;52:1213–1225. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

