Formulation optimization of lyophilized aptamer-gold nanoparticles: Maintained colloidal stability and cellular uptake
- PMID: 38774322
- PMCID: PMC11107208
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30743
Formulation optimization of lyophilized aptamer-gold nanoparticles: Maintained colloidal stability and cellular uptake
Abstract
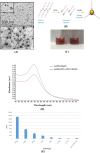
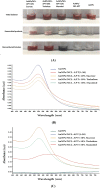
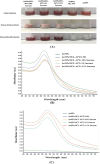
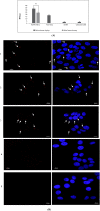
Anti-nucleolin (NCL) aptamer AS1411 is the first anticancer aptamer tested in clinical trials. Gold nanoparticles (AuNP) have been widely exploited for various biomedical applications due to their unique functional properties. In this study, we evaluated the colloidal stability and targeting capacity of AS1411-funtionalized AuNP (AuNP/NCL-Apt) against MCF-7 breast cancer cell line before and after lyophilization. Trehalose, mannitol, and sucrose at various concentrations were evaluated to determine their cryoprotection effects. Our results indicate that sucrose at 10 % (w/v) exhibits the best cryoprotection effect and minimal AuNP/NCL-Apt aggregation as confirmed by UV-Vis spectroscopy and dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements. Moreover, the lyophilized AuNP/NCL-Apt at optimized formulation maintained its targeting and cytotoxic functionality against MCF-7 cells as proven by the cellular uptake assays utilizing flow cytometry and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). Quantitative PCR (qPCR) analysis of nucleolin-target gene expression also confirmed the effectiveness of AuNP/NCL-Apt. This study highlights the importance of selecting the proper type and concentration of cryoprotectant in the typical nanoparticle lyophilization process and contributes to our understanding of the physical and biological properties of functionalized nanoparticles upon lyophilization.
Keywords: Aggregation; Aptamer; Cryoprotectants; Gold nanoparticles; Lyophilization.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Blair J. Making magic bullets. Nat Microbiol. 2017;2 - PubMed
-
- Farokhzad O.C., Langer R. Impact of nanotechnology on drug delivery. ACS Nano. 2009;3(1):16–20. - PubMed
-
- Alshaer W., Hillaireau H., Fattal E. Aptamer-guided nanomedicines for anticancer drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018;134:122–137. - PubMed
-
- Alkilany A.M., et al. Ligand density on nanoparticles: a parameter with critical impact on nanomedicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019;143:22–36. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

