Improving systemic therapy selection for inflammatory skin diseases: A clinical need survey
- PMID: 38774343
- PMCID: PMC11107249
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdin.2024.03.019
Improving systemic therapy selection for inflammatory skin diseases: A clinical need survey
Abstract
Background: Empirical decisions to select therapies for psoriasis (PSO) and atopic dermatitis (AD) can lead to delays in disease control and increased health care costs. However, routine molecular testing for AD and PSO are lacking.
Objective: To examine (1) how clinicians choose systemic therapies for patients with PSO and AD without molecular testing and (2) to determine how often the current approach leads to patients switching medications.
Methods: A 20-question survey designed to assess clinician strategies for systemic treatment of AD and PSO was made available to attendees of a national dermatology conference in 2022.
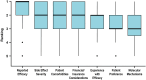
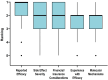
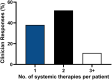
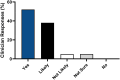
Results: Clinicians participating in the survey (265/414, 64% response rate) ranked "reported efficacy" as the most important factor governing treatment choice (P < .001). However, 62% (165/265) of clinicians estimated that 2 or more systemic medications were typically required to achieve efficacy. Over 90% (239/265) of respondents would or would likely find a molecular test to guide therapeutic selection useful.
Limitations: To facilitate ease of recall, questions focused on systemic therapies as a whole and not individual therapies.
Conclusion: Clinicians want a molecular test to help determine the most efficacious drug for individual patients.
Keywords: atopic dermatitis; biologics; gene expression profile test; inflammatory skin disease; molecular; precision medicine; psoriasis; response to therapy; systemic therapy.
© 2024 by the American Academy of Dermatology, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Brownstone received a stipend paid for by Castle Biosciences, Inc. Dr Farberg is a consultant for Castle Biosciences, Inc and on the advisory board for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Pfizer, and Sun Pharma. Drs Quick, Siegel, Hurton, and Goldberg are employees and option and stockholders for Castle Biosciences, Inc. Dr Lio reports research grants/funding from AbbVie, AOBiome, Eczema Foundation, National Eczema Association; is on the speaker's bureau for AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Galderma, Hyphens Pharma, Incyte, La Roche-Posay/L’Oreal, MyOR Diagnostics, ParentMD, Pfizer, Pierre-Fabre Dermatologie, and Regeneron/Sanofi Genzyme; reports consulting/advisory boards for AbbVie, Almirall, Amyris, Arbonne, ASLAN, Bodewell, Boston Skin Science, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Burt’s Bees, Castle Biosciences, Codex Labs, Concerto Biosci, Dermavant, Dermira, DermVeda, Eli Lilly, Galderma, IntraDerm, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, Kaleido Biosci, Kimberly Clark, LEO Pharma, Lipidor, L’Oreal, Menlo Therapeutics, Merck, Micreos, MyOR Diagnostics, Regeneron/Sanofi Genzyme, Sibel Health, Skinfix, Sonica, Theraplex, UCB, Unilever, Verrica, and Yobee Care; reports stock options with LearnSkin/Learn Health, Medable, Micreos, Modernizing Medicine, and Yobee Care. In addition, Dr Lio has a patent pending for a Theraplex product with royalties paid and is a Board member and Scientific Advisory Committee Member of the National Eczema Association. Author Litchman has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
New onset atopic dermatitis and psoriasis in the same patients under biologic treatments: The role of systemic treatments as a possible trigger.Dermatol Ther. 2022 Nov;35(11):e15814. doi: 10.1111/dth.15814. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Dermatol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36088634
-
Ultraviolet Phototherapy Management of Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: An Evidence-Based Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009;9(27):1-66. Epub 2009 Nov 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009. PMID: 23074532 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of comorbidities in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis in the French population.Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2021 Mar;148(1):28-33. doi: 10.1016/j.annder.2020.02.015. Epub 2021 Jan 23. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2021. PMID: 33500190
-
A Treatment Algorithm for Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis in Adults.J Cutan Med Surg. 2018 Jan/Feb;22(1):78-83. doi: 10.1177/1203475417733460. Epub 2017 Oct 28. J Cutan Med Surg. 2018. PMID: 29082775 Review.
-
Facing psoriasis and atopic dermatitis: are there more similarities or more differences?Eur J Dermatol. 2008 Mar-Apr;18(2):172-80. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2008.0357. Eur J Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18424378 Review.
Cited by
-
A drug delivery perspective on nanotechnology-based topical therapeutics for inflammatory skin diseases.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025 Jun;20(12):1441-1459. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2025.2506347. Epub 2025 May 25. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40415475 Review.
-
Exploring the Link Between Atopic Dermatitis and Eosinophilic Esophagitis.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2025 Mar;18(3):15-20. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40135176 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

