An HPLC-SEC-based rapid quantification method for vesicular stomatitis virus particles to facilitate process development
- PMID: 38774583
- PMCID: PMC11107205
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101252
An HPLC-SEC-based rapid quantification method for vesicular stomatitis virus particles to facilitate process development
Erratum in
-
Erratum: An HPLC-SEC-based rapid quantification method for vesicular stomatitis virus particles to facilitate process development.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024 Sep 12;32(4):101335. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101335. eCollection 2024 Dec 12. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024. PMID: 39309262 Free PMC article.
Abstract
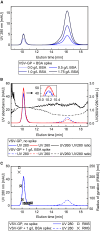
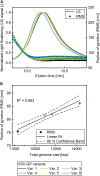
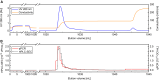
Virus particle (VP) quantification plays a pivotal role in the development of production processes of VPs for virus-based therapies. The yield based on total VP count serves as a process performance indicator for evaluating process efficiency and consistency. Here, a label-free particle quantification method for enveloped VPs was developed, with potential applications in oncolytic virotherapy, vaccine development, and gene therapy. The method comprises size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) separation using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) instruments. Ultraviolet (UV) was used for particle quantification and multi-angle light scattering (MALS) for particle characterization. Consistent recoveries of over 97% in the SEC were achieved upon mobile phase screenings and addition of bovine serum albumin (BSA) as sample stabilizer. A calibration curve was generated, and the method's performance and applicability to in-process samples were characterized. The assay's repeatability variation was <1% and its intermediate precision variation was <3%. The linear range of the method spans from 7.08 × 108 to 1.72 × 1011 VP/mL, with a limit of detection (LOD) of 7.72 × 107 VP/mL and a lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) of 4.20 × 108 VP/mL. The method, characterized by its high precision, requires minimal hands-on time and provides same-day results, making it efficient for process development.
Keywords: HPLC; VSV-GP; analytical SEC; vesicular stomatitis virus; virus particle quantification.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- U.S. National Library of Medicine Oncolytic viruses in clinical trials, search terms: “gene therapies” AND “virus”, and “oncolytic virus”. 2023. clinicaltrials.gov
-
- Singh N., Heldt C.L. Challenges in downstream purification of gene therapy viral vectors. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2022;35 doi: 10.1016/j.coche.2021.100780. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

