What does artificial intelligence mean in rheumatology?
- PMID: 38774703
- PMCID: PMC11104749
- DOI: 10.46497/ArchRheumatol.2024.10664
What does artificial intelligence mean in rheumatology?
Abstract
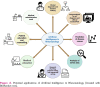
Intelligence is the ability of humans to learn from experiences to ascribe conscious weights and unconscious biases to modulate their outputs from given inputs. Transferring this ability to computers is artificial intelligence (AI). The ability of computers to understand data in an intelligent manner is machine learning. When such learning is with images and videos, which involves deeper layers of artificial neural networks, it is described as deep learning. Large language models are the latest development in AI which incorporate self-learning into deep learning through transformers. AI in Rheumatology has immense potential to revolutionize healthcare and research. Machine learning could aid clinical diagnosis and decision-making, and deep learning could extend this to analyze images of radiology or positron emission tomography scans or histopathology images to aid a clinician's diagnosis. Analysis of routinely obtained patient data or continuously collected information from wearables could predict disease flares. Analysis of high-volume genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, or metabolomics data from patients could help identify novel markers of disease prognosis. AI might identify newer therapeutic targets based on in-silico modelling of omics data. AI could help automate medical administrative work such as inputting information into electronic health records or transcribing clinic notes. AI could help automate patient education and counselling. Beyond the clinic, AI has the potential to aid medical education. The ever-expanding capabilities of AI models bring along with them considerable ethical challenges, particularly related to risks of misuse. Nevertheless, the widespread use of AI in Rheumatology is inevitable and a progress with great potential.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; deep learning; image analysis machine learning; rheumatology.
Copyright © 2024, Turkish League Against Rheumatism.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging: From Computer Science to Machine and Deep Learning.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 1;16(21):3702. doi: 10.3390/cancers16213702. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39518140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning in women's health nursing.Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2020 Mar 31;26(1):5-9. doi: 10.4069/kjwhn.2020.03.11. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2020. PMID: 36311852 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis of Oral Diseases: Applications and Pitfalls.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Apr 19;12(5):1029. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12051029. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revolutionizing Breast Healthcare: Harnessing the Role of Artificial Intelligence.Cureus. 2023 Dec 8;15(12):e50203. doi: 10.7759/cureus.50203. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38192969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Pharmacological Research: Bridging the Gap Between Data and Drug Discovery.Cureus. 2023 Aug 30;15(8):e44359. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44359. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37779744 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the Performance of Large Language Models in the Management of Axial Spondyloarthropathy: Analysis of EULAR 2022 Recommendations.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jun 7;15(12):1455. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15121455. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564776 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative performance of artificial intelligence models in rheumatology board-level questions: evaluating Google Gemini and ChatGPT-4o.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 Nov;43(11):3507-3513. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07154-5. Epub 2024 Sep 28. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39340572
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources