PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway Mediated Autophagy in Oral Carcinoma - A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 38774756
- PMCID: PMC11103401
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.94566
PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway Mediated Autophagy in Oral Carcinoma - A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
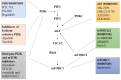
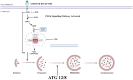
Oral cancer is the most heterogeneous cancer at clinical and histological levels. PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway was identified as one of the most commonly modulated signals in oral cancer, which regulates major cellular and metabolic activity of the cell. Thus, various proteins of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway were used as therapeutic targets for oral cancer, to design more specific drugs with less off-target toxicity. This review sheds light on the regulation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR, and its role in controlling autophagy and associated apoptosis during the progression and metastasis of oral squamous type of malignancy (OSCC). In addition, we reviewed in detail the upstream activators and the downstream effectors of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling as potential therapeutic targets for oral cancer treatment.
Keywords: PI3K/AKT; autophagy; metastasis; oral cancer.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Ferreira e Costa R, Leão ML, Sant'Ana MS, Mesquita RA, Gomez RS, Santos-Silva AR, Khurram SA, Tailor A, Schouwstra CM, Robinson L, van Heerden WF. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Frequency in Young Patients from Referral Centers Around the World. Head and Neck Pathology. 2022 Sep;16(3):755–62. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

