Global trends in Cryptococcus and its interactions with the host immune system: a bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 38774865
- PMCID: PMC11106374
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1397338
Global trends in Cryptococcus and its interactions with the host immune system: a bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Objectives: This manuscript undertakes a systematic examination of the research landscape concerning global Cryptococcus species and their dynamism with the host immune system spanning the past decade. It furnishes a detailed survey of leading knowledge institutions and critical focal points in this area, utilizing bibliometric analysis.
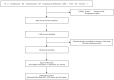
Methods: VOSviewer and CiteSpace software platforms were employed to systematically analyze and graphically depict the relevant literature indexed in the WoSCC database over the preceding ten years.
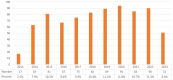
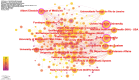
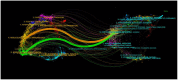
Results: In the interval between October 1, 2013, and October 1, 2023, a corpus of 795 publications was amassed. The primary research institutions involved in this study include Duke University, the University of Minnesota, and the University of Sydney. The leading trio of nations, in terms of publication volume, comprises the United States, China, and Brazil. Among the most prolific authors are Casadevall, Arturo; Wormley, Floyd L., Jr.; and Olszewski, Michal A., with the most highly cited author being Perfect, Jr. The most esteemed journal is Mbio, while Infection and Immunity commands the highest citation frequency, and the Journal of Clinical Microbiology boasts the most significant impact factor. Present research foci encompass the intricate interactions between Cryptococcus pathogenesis and host immunity, alongside immune mechanisms, complications, and immunotherapies.
Conclusion: This represents the first exhaustive scholarly review and bibliometric scrutiny of the evolving landscapes in Cryptococcus research and its interactions with the host immune system. The analyses delineated herein provide insights into prevailing research foci and trajectories, thus furnishing critical directions for subsequent inquiries in this domain.
Keywords: Cryptococcus spp.; bibliometric analysis; cryptococcosis; host immune responses; visualization techniques.
Copyright © 2024 Tang, Hao, Liu, He, Tian, Jing, Liu, Xu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Villena SN, Pinheiro RO, Pinheiro CS, Nunes MP, Takiya CM, DosReis GA, et al. Capsular polysaccharides galactoxylomannan and glucuronoxylomannan from Cryptococcus neoformans induce macrophage apoptosis mediated by Fas ligand. Cell Microbiol. (2008) 10:1274–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01125.x - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

