Transcriptomic and spatial dissection of human ex vivo right atrial tissue reveals proinflammatory microvascular changes in ischemic heart disease
- PMID: 38776872
- PMCID: PMC11148807
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101556
Transcriptomic and spatial dissection of human ex vivo right atrial tissue reveals proinflammatory microvascular changes in ischemic heart disease
Abstract
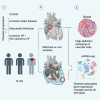
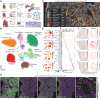
Cardiovascular disease plays a central role in the electrical and structural remodeling of the right atrium, predisposing to arrhythmias, heart failure, and sudden death. Here, we dissect with single-nuclei RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) and spatial transcriptomics the gene expression changes in the human ex vivo right atrial tissue and pericardial fluid in ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, and ischemic and non-ischemic heart failure using asymptomatic patients with valvular disease who undergo preventive surgery as the control group. We reveal substantial differences in disease-associated gene expression in all cell types, collectively suggesting inflammatory microvascular dysfunction and changes in the right atrial tissue composition as the valvular and vascular diseases progress into heart failure. The data collectively suggest that investigation of human cardiovascular disease should expand to all functionally important parts of the heart, which may help us to identify mechanisms promoting more severe types of the disease.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; disease mechanism; genetic variation; heart; heart failure; inflammation; ischemic heart disease; single cell; spatial transcriptomics; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Wang L., Yu P., Zhou B., Song J., Li Z., Zhang M., Guo G., Wang Y., Chen X., Han L., Hu S. Single-cell reconstruction of the adult human heart during heart failure and recovery reveals the cellular landscape underlying cardiac function. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020;22:108–119. - PubMed
-
- Nicin L., Schroeter S.M., Glaser S.F., Schulze-Brüning R., Pham M.-D., Hille S.S., Yekelchyk M., Kattih B., Abplanalp W.T., Tombor L., et al. A human cell atlas of the pressure-induced hypertrophic heart. Nat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022;1:174–185.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

