Venetoclax acts as an immunometabolic modulator to potentiate adoptive NK cell immunotherapy against leukemia
- PMID: 38776913
- PMCID: PMC11228450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101580
Venetoclax acts as an immunometabolic modulator to potentiate adoptive NK cell immunotherapy against leukemia
Abstract
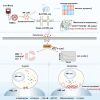
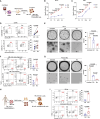
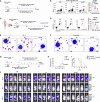
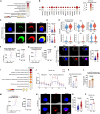
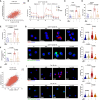
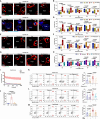
Natural killer (NK) cell-based immunotherapy holds promise for cancer treatment; however, its efficacy remains limited, necessitating the development of alternative strategies. Here, we report that venetoclax, an FDA-approved BCL-2 inhibitor, directly activates NK cells, enhancing their cytotoxicity against acute myeloid leukemia (AML) both in vitro and in vivo, likely independent of BCL-2 inhibition. Through comprehensive approaches, including bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing, avidity measurement, and functional assays, we demonstrate that venetoclax increases the avidity of NK cells to AML cells and promotes lytic granule polarization during immunological synapse (IS) formation. Notably, we identify a distinct CD161lowCD218b+ NK cell subpopulation that exhibits remarkable sensitivity to venetoclax treatment. Furthermore, venetoclax promotes mitochondrial respiration and ATP synthesis via the NF-κB pathway, thereby facilitating IS formation in NK cells. Collectively, our findings establish venetoclax as a multifaceted immunometabolic modulator of NK cell function and provide a promising strategy for augmenting NK cell-based cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: NF-κB; RNA sequencing; acute myeloid leukemia; avidity; cytotoxicity; immunological synapse; immunotherapy; mitochondrial respiration; natural killer cells; venetoclax.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

