The impact of inversions across 33,924 families with rare disease from a national genome sequencing project
- PMID: 38776926
- PMCID: PMC11179413
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2024.04.018
The impact of inversions across 33,924 families with rare disease from a national genome sequencing project
Abstract
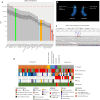
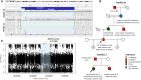
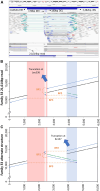
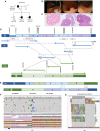
Detection of structural variants (SVs) is currently biased toward those that alter copy number. The relative contribution of inversions toward genetic disease is unclear. In this study, we analyzed genome sequencing data for 33,924 families with rare disease from the 100,000 Genomes Project. From a database hosting >500 million SVs, we focused on 351 genes where haploinsufficiency is a confirmed disease mechanism and identified 47 ultra-rare rearrangements that included an inversion (24 bp to 36.4 Mb, 20/47 de novo). Validation utilized a number of orthogonal approaches, including retrospective exome analysis. RNA-seq data supported the respective diagnoses for six participants. Phenotypic blending was apparent in four probands. Diagnostic odysseys were a common theme (>50 years for one individual), and targeted analysis for the specific gene had already been performed for 30% of these individuals but with no findings. We provide formal confirmation of a European founder origin for an intragenic MSH2 inversion. For two individuals with complex SVs involving the MECP2 mutational hotspot, ambiguous SV structures were resolved using long-read sequencing, influencing clinical interpretation. A de novo inversion of HOXD11-13 was uncovered in a family with Kantaputra-type mesomelic dysplasia. Lastly, a complex translocation disrupting APC and involving nine rearranged segments confirmed a clinical diagnosis for three family members and resolved a conundrum for a sibling with a single polyp. Overall, inversions play a small but notable role in rare disease, likely explaining the etiology in around 1/750 families across heterogeneous clinical cohorts.
Keywords: APC; HOXD cluster; MECP2; MSH2; PacBio; RNA-seq; complex rearrangement; founder mutation; genome sequencing; inversion.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests H.H.U. declares research support or consultancy fees from Janssen, UCB Pharma, GSK, Eli Lilly, Bristol Myers Squibb BMS, OMass and Mestag. J.Y. is now employed by Novo Nordisk.
Figures



References
-
- Feuk L., Carson A.R., Scherer S.W. Structural variation in the human genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006;7:85–97. - PubMed
-
- Jacquemont M.L., Sanlaville D., Redon R., Raoul O., Cormier-Daire V., Lyonnet S., Amiel J., Le Merrer M., Heron D., de Blois M.C., et al. Array-based comparative genomic hybridisation identifies high frequency of cryptic chromosomal rearrangements in patients with syndromic autism spectrum disorders. J. Med. Genet. 2006;43:843–849. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Miller D.T., Adam M.P., Aradhya S., Biesecker L.G., Brothman A.R., Carter N.P., Church D.M., Crolla J.A., Eichler E.E., Epstein C.J., et al. Consensus statement: chromosomal microarray is a first-tier clinical diagnostic test for individuals with developmental disabilities or congenital anomalies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010;86:749–764. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

