Phase separation of SPIN1 through its IDR facilitates histone methylation readout and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 38777743
- PMCID: PMC11630302
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjae024
Phase separation of SPIN1 through its IDR facilitates histone methylation readout and tumorigenesis
Abstract
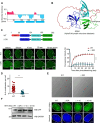
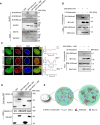
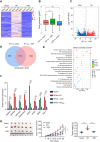
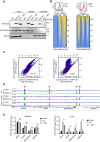
Spindlin1 (SPIN1) is a unique multivalent histone modification reader that plays a role in ribosomal RNA transcription, chromosome segregation, and tumorigenesis. However, the function of the extended N-terminal region of SPIN1 remains unclear. Here, we demonstrated that SPIN1 can form phase-separated and liquid-like condensates both in vitro and in vivo through its N-terminal intrinsically disordered region (IDR). The phase separation of SPIN1 recruits the histone methyltransferase MLL1 to the same condensates and enriches the H3K4 methylation marks. This process also facilitates the binding of SPIN1 to H3K4me3 and activates tumorigenesis-related genes. Moreover, SPIN1-IDR enhances the genome-wide chromatin binding of SPIN1 and facilitates its localization to genes associated with the MAPK signaling pathway. These findings provide new insights into the biological function of the IDR in regulating SPIN1 activity and reveal a previously unrecognized role of SPIN1-IDR in histone methylation readout. Our study uncovers the crucial role of appropriate biophysical properties of SPIN1 in facilitating gene expression and links phase separation to tumorigenesis, which provides a new perspective for understanding the function of SPIN1.
Keywords: IDR; SPIN1; histone methylation reader; phase separation; tumorigenesis.
© The Author(s) (2024). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, CEMCS, CAS.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nucleolar localization signal and histone methylation reader function is required for SPIN1 to promote rRNA gene expression.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Oct 20;505(1):325-332. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.098. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 30249398
-
A transcriptional coregulator, SPIN·DOC, attenuates the coactivator activity of Spindlin1.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 22;292(51):20808-20817. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.814913. Epub 2017 Oct 23. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29061846 Free PMC article.
-
Histone code reader SPIN1 is a promising target of cancer therapy.Biochimie. 2021 Dec;191:78-86. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2021.09.002. Epub 2021 Sep 4. Biochimie. 2021. PMID: 34492335 Review.
-
Molecular basis underlying histone H3 lysine-arginine methylation pattern readout by Spin/Ssty repeats of Spindlin1.Genes Dev. 2014 Mar 15;28(6):622-36. doi: 10.1101/gad.233239.113. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 24589551 Free PMC article.
-
SET/MLL family proteins in hematopoiesis and leukemia.Int J Hematol. 2017 Jan;105(1):7-16. doi: 10.1007/s12185-016-2118-8. Epub 2016 Oct 31. Int J Hematol. 2017. PMID: 27796741 Review.
Cited by
-
SPIN1 facilitates chemoresistance and HR repair by promoting Tip60 binding to H3K9me3.EMBO Rep. 2024 Sep;25(9):3970-3989. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00219-1. Epub 2024 Aug 1. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 39090319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberti S., Dormann D. (2019). Liquid–liquid phase separation in disease. Annu. Rev. Genet. 53, 171–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

