Baricitinib Improvement Across Regions in Atopic Dermatitis Patients with Baseline Body Surface Area up to 40% and Severe Itch
- PMID: 38777937
- PMCID: PMC11169304
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-024-01171-7
Baricitinib Improvement Across Regions in Atopic Dermatitis Patients with Baseline Body Surface Area up to 40% and Severe Itch
Abstract
Introduction: Patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) who are most likely to respond to the Janus kinase (JAK) 1/2 inhibitor baricitinib (BARI) are known to have an impacted body surface area (BSA) ≤ 40% and severe itch (numerical rating scale [NRS] ≥ 7], collectively termed 'BARI itch-dominant' patients. Our objective is to build on our previous work by providing a body region-specific, clinical characterization of the BARI itch-dominant patient at baseline and their response to BARI 4 mg.
Methods: BREEZE-AD7 was a phase 3 trial in adults with moderate-to-severe AD receiving placebo or 2 mg or 4 mg BARI in combination with topical corticosteroids. Assessing only data from BARI itch-dominant patients, we summarized the baseline characteristics and conducted body region-specific analyses on Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) data in order to report the response to placebo versus BARI 4 mg within this patient subtype.
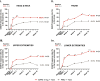
Results: BARI 4 mg was highly effective across all body regions; at week 16, 75% improvement was seen in EASI scores (EASI75), and response rates with BARI 4 mg (head/neck, 58.3%; trunk, 69.2%; upper extremities, 61.5%; lower extremities, 87.5%) all exceeded those with placebo (head/neck: 37.5%; trunk, 40.6%; upper extremities, 18.8%; lower extremities, 40.6%) as well as the overall EASI75 rates of the intent-to-treat (ITT) population (BARI, 48.0%; placebo, 23.0%). At baseline, most BARI itch-dominant patients presented with involvement of all regions (mean regional BSA 22.7%-40.3%), highest in the head and neck, mean EASI region scores of 15.7-24.0, and considerably severe sign ratings (mean EASI sub-scores: 1.4-2.3, out of 3), especially for erythema.
Conclusion: BARI itch-dominant patients exhibit AD involvement across all body regions and considerable sign severity, especially erythema. In response to BARI 4 mg, EASI quickly improved across regions, substantially more so in this subtype than in the ITT population.
Keywords: Atopic dermatitis; Baricitinib; Body surface area; Eczema Area and Severity Index; Itch-dominant; Janus kinase; Regional analysis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Jose Manuel Carrascosa has received grants, consulting fees, speaker honoraria, travel support and/or served on an advisory board for AbbVie, Almirall, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly and Company, Galderma, Janssen, IB Pharma, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz, Sanofi, and UCB. Alessandra Narcisi has received consulting fees, speaker honoraria, and/or travel support from AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Boehringer, Eli Lilly and Company, LEO Pharma, Pfizer, Sanofi, and UCB. Toshifumi Nomura has received speaker honoraria from Eli Lilly and Company. Sonja Ständer has received grants, consulting fees, speaker honoraria, travel support, and/or served on an advisory board for AbbVie, Almirall, Beiersdorf, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Clexio, Eli Lilly and Company, Escient, FomF, Galderma, Grünenthal, Incyte, IntegrityCE, Kiniksa, Klinge Pharma, LEO Pharma, L’Oreal, MEDahead, Moroscience, Novartis, Pfizer, P.G. Unna Academy, Sanofi, TouchIME, Vifor, and WebMD. Christian Vestergaard has received consulting fees, speaker honoraria, and/or research support from AbbVie, Eli Lilly and Company, LEO Pharma, Novartis, and Sanofi. Silvia Sabatino, Susanne Grond, Uffe Koppelhus, Mohamed Elrayes, and Yun-Fei Chen are employees and minor shareholders of Eli Lilly and Company. Chunyuan Liu is an employee of TigerMed-BDM Inc. and under long-term contract as a statistical expert for Eli Lilly and Company. Andrea Wollenberg has received grants, consulting fees, and/or study support from AbbVie, Aileens, Almirall, Beiersdorf, Eli Lilly and Company, Galapagos, Galderma, Glenmark, GSK, Janssen, LEO Pharma, L’Oreal, MedImmune, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Regeneron, Sanofi, and UCB. Chunyuan Liu is an employee of TigerMed-BDM Inc and under contract with Eli Lilly and Company. He is not a Lilly shareholder.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

