Deletion of IRE1α in podocytes exacerbates diabetic nephropathy in mice
- PMID: 38778209
- PMCID: PMC11111796
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-62599-7
Deletion of IRE1α in podocytes exacerbates diabetic nephropathy in mice
Abstract
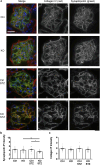
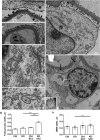
Protein misfolding in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of podocytes contributes to the pathogenesis of glomerular diseases. Protein misfolding activates the unfolded protein response (UPR), a compensatory signaling network. We address the role of the UPR and the UPR transducer, inositol-requiring enzyme 1α (IRE1α), in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in mice. Diabetes caused progressive albuminuria in control mice that was exacerbated in podocyte-specific IRE1α knockout (KO) mice. Compared to diabetic controls, diabetic IRE1α KO mice showed reductions in podocyte number and synaptopodin. Glomerular ultrastructure was altered only in diabetic IRE1α KO mice; the major changes included widening of podocyte foot processes and glomerular basement membrane. Activation of the UPR and autophagy was evident in diabetic control, but not diabetic IRE1α KO mice. Analysis of human glomerular gene expression in the JuCKD-Glom database demonstrated induction of genes associated with the ER, UPR and autophagy in diabetic nephropathy. Thus, mice with podocyte-specific deletion of IRE1α demonstrate more severe diabetic nephropathy and attenuation of the glomerular UPR and autophagy, implying a protective effect of IRE1α. These results are consistent with data in human diabetic nephropathy and highlight the potential for therapeutically targeting these pathways.
Keywords: Albuminuria; Autophagy; Endoplasmic reticulum; Gene expression; Glomerulopathy; Unfolded protein response.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Deletion of inositol-requiring enzyme-1α in podocytes disrupts glomerular capillary integrity and autophagy.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Jun 15;28(12):1636-1651. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-12-0828. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28428258 Free PMC article.
-
The unfolded protein response transducer IRE1α promotes reticulophagy in podocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022 Jun 1;1868(6):166391. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2022.166391. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022. PMID: 35304860
-
Genetic deletion of calcium-independent phospholipase A2γ protects mice from diabetic nephropathy.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 31;19(10):e0311404. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311404. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39480824 Free PMC article.
-
The IRE1α pathway in glomerular diseases: The unfolded protein response and beyond.Front Mol Med. 2022 Sep 26;2:971247. doi: 10.3389/fmmed.2022.971247. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 39086958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond UPR: cell-specific roles of ER stress sensor IRE1α in kidney ischemic injury and transplant rejection.Kidney Int. 2023 Sep;104(3):463-469. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2023.06.016. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Kidney Int. 2023. PMID: 37391039 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research hotspots and frontiers of endoplasmic reticulum in glomerular podocytes: a bibliometric and visual analysis from 2005 to 2023.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1488340. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1488340. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39840101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- KDIGO Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Glomerulonephritis Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012;2:139–274.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

