Genome-wide characterisation of HD-Zip transcription factors and functional analysis of PbHB24 during stone cell formation in Chinese white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri)
- PMID: 38778247
- PMCID: PMC11112822
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-024-05138-w
Genome-wide characterisation of HD-Zip transcription factors and functional analysis of PbHB24 during stone cell formation in Chinese white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri)
Abstract
Background: The homodomain-leucine zipper (HD-Zip) is a conserved transcription factor family unique to plants that regulate multiple developmental processes including lignificaion. Stone cell content is a key determinant negatively affecting pear fruit quality, which causes a grainy texture of fruit flesh, because of the lignified cell walls.
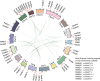
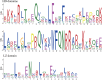
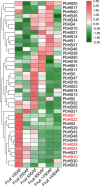
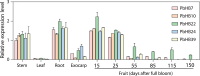
Results: In this study, a comprehensive bioinformatics analysis of HD-Zip genes in Chinese white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) (PbHBs) was performed. Genome-wide identification of the PbHB gene family revealed 67 genes encoding PbHB proteins, which could be divided into four subgroups (I, II, III, and IV). For some members, similar intron/exon structural patterns support close evolutionary relationships within the same subgroup. The functions of each subgroup of the PbHB family were predicted through comparative analysis with the HB genes in Arabidopsis and other plants. Cis-element analysis indicated that PbHB genes might be involved in plant hormone signalling and external environmental responses, such as light, stress, and temperature. Furthermore, RNA-sequencing data and quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) verification revealed the regulatory roles of PbHB genes in pear stone cell formation. Further, co-expression network analysis revealed that the eight PbHB genes could be classified into different clusters of co-expression with lignin-related genes. Besides, the biological function of PbHB24 in promoting stone cell formation has been demonstrated by overexpression in fruitlets.
Conclusions: This study provided the comprehensive analysis of PbHBs and highlighted the importance of PbHB24 during stone cell development in pear fruits.
Keywords: Genome-wide analysis; HD-Zip; Lignin; Pear; Stone cell; Transcription factor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of bZIP transcription factors and their expression profile under abiotic stresses in Chinese pear (Pyrus bretschneideri).BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Sep 9;21(1):413. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03191-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34503442 Free PMC article.
-
PbrMYB169 positively regulates lignification of stone cells in pear fruit.J Exp Bot. 2019 Mar 27;70(6):1801-1814. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz039. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 30715420
-
Integrative Analysis of the Core Fruit Lignification Toolbox in Pear Reveals Targets for Fruit Quality Bioengineering.Biomolecules. 2019 Sep 18;9(9):504. doi: 10.3390/biom9090504. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31540505 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification, Evolution and Functional Divergence of MYB Transcription Factors in Chinese White Pear (Pyrus bretschneideri).Plant Cell Physiol. 2016 Apr;57(4):824-47. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcw029. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26872835
-
Genome-wide analysis of WRKY transcription factors in white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) reveals evolution and patterns under drought stress.BMC Genomics. 2015 Dec 24;16:1104. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2233-6. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26704366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yufei W, Ahmad N, Jiaxin C, Lili Y, Yuying H, Nan W, Min Z, Libo J, Na Y, Xiuming L. CtDREB52 transcription factor regulates UV-B-induced flavonoid biosynthesis by transactivating CtMYB and CtF3′H in Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L) Plant Stress. 2024;11:100384. doi: 10.1016/j.stress.2024.100384. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

