Human insulin as both antigen and protector in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 38778498
- PMCID: PMC11563931
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.202350949
Human insulin as both antigen and protector in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
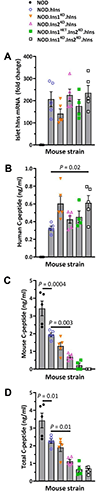
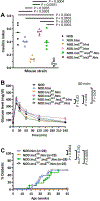
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is characterized by T-cell responses to islet antigens. Investigations in humans and the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse model of T1D have revealed that T-cell reactivity to insulin plays a central role in the autoimmune response. As there is no convenient NOD-based model to study human insulin (hIns) or its T-cell epitopes in the context of spontaneous T1D, we developed a NOD mouse strain transgenically expressing hIns in islets under the control of the human regulatory region. Female NOD.hIns mice developed T1D at approximately the same rate and overall incidence as NOD mice. Islet-infiltrating T cells from NOD.hIns mice recognized hIns peptides; both CD8 and CD4 T-cell epitopes were identified. We also demonstrate that islet-infiltrating T cells from HLA-transgenic NOD.hIns mice can be used to identify potentially patient-relevant hIns T-cell epitopes. Besides serving as an antigen, hIns was expressed in the thymus of NOD.hIns mice and could serve as a protector against T1D under certain circumstances, as previously suggested by genetic studies in humans. NOD.hIns mice and related strains facilitate human-relevant epitope discovery efforts and the investigation of fundamental questions that cannot be readily addressed in humans.
Keywords: Animal models; Autoimmunity; CD8 T cells; MHC; Transgenic models.
© 2024 Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Dale L. Greiner consults for, and receives research support from, The Jackson Laboratory. All other authors have no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Beyond HLA-A*0201: new HLA-transgenic nonobese diabetic mouse models of type 1 diabetes identify the insulin C-peptide as a rich source of CD8+ T cell epitopes.J Immunol. 2012 Jun 1;188(11):5766-75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102930. Epub 2012 Apr 25. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22539795 Free PMC article.
-
Thymic and postthymic regulation of diabetogenic CD8 T cell development in TCR transgenic nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice.J Immunol. 2000 May 15;164(10):5466-73. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.10.5466. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10799914
-
Regulation of diabetes development by regulatory T cells in pancreatic islet antigen-specific TCR transgenic nonobese diabetic mice.J Immunol. 2002 Jun 15;168(12):6159-64. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.12.6159. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12055228
-
Identifying New Hybrid Insulin Peptides (HIPs) in Type 1 Diabetes.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 30;12:667870. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.667870. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33995402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T-cell epitopes in type 1 diabetes.Curr Diab Rep. 2004 Apr;4(2):87-94. doi: 10.1007/s11892-004-0062-0. Curr Diab Rep. 2004. PMID: 15035967 Review.
Cited by
-
Using GeoMx DSP Spatial Proteomics to Investigate Immune Infiltration of NOD Mouse Islet and Exocrine Compartments.Mol Imaging Biol. 2024 Dec;26(6):943-954. doi: 10.1007/s11307-024-01961-7. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Mol Imaging Biol. 2024. PMID: 39557779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jaeckel E, Lipes MA and von Boehmer H, Recessive tolerance to preproinsulin 2 reduces but does not abolish type 1 diabetes. Nat. Immunol 2004. 5: 1028–1035. - PubMed
-
- Skowera A, Ellis RJ, Varela-Calvino R, Arif S, Huang GC, Van-Krinks C, Zaremba A, Rackham C, Allen JS, Tree TIM, Zhao M, Dayan CM, Sewell AK, Unger W, Drijfhout JW, Ossendorp F, Roep BO and Peakman M, CTLs are targeted to kill β cells in patients with type 1 diabetes through recognition of a glucose-regulated preproinsulin epitope. J. Clin. Invest 2008. 118: 3390–3402. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

