Inhibitory modulation of speech trajectories: Evidence from a vowel-modified Stroop task
- PMID: 38778635
- PMCID: PMC11269046
- DOI: 10.1080/02643294.2024.2315831
Inhibitory modulation of speech trajectories: Evidence from a vowel-modified Stroop task
Abstract
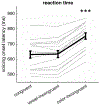
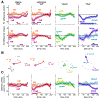
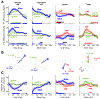
How does cognitive inhibition influence speaking? The Stroop effect is a classic demonstration of the interference between reading and color naming. We used a novel variant of the Stroop task to measure whether this interference impacts not only the response speed, but also the acoustic properties of speech. Speakers named the color of words in three categories: congruent (e.g., red written in red), color-incongruent (e.g., green written in red), and vowel-incongruent - those with partial phonological overlap with their color (e.g., rid written in red, grain in green, and blow in blue). Our primary aim was to identify any effect of the distractor vowel on the acoustics of the target vowel. Participants were no slower to respond on vowel-incongruent trials, but formant trajectories tended to show a bias away from the distractor vowel, consistent with a phenomenon of acoustic inhibition that increases contrast between confusable alternatives.
Keywords: Speech; Stroop; competition; inhibition; vowels.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures

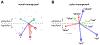
References
-
- Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, & Walker S (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67(1), 1–48.
-
- Benjamini Y, & Hochberg Y (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 57(1), 289–300.
-
- Berent I, & Marom M (2005). Skeletal structure of printed words: Evidence from the Stroop task. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 31(2), 328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
