Partial hand replantation using free microsurgical replantation with staged heterotopic banking of amputated parts: towards improving long term outcomes
- PMID: 38778864
- PMCID: PMC11110872
- DOI: 10.1080/23320885.2024.2350471
Partial hand replantation using free microsurgical replantation with staged heterotopic banking of amputated parts: towards improving long term outcomes
Abstract
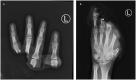
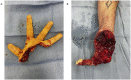
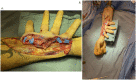
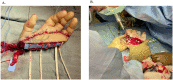
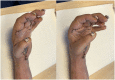
In hand trauma, the uninjured forearm has been touted as the ideal site for ectopic banking in digit/hand amputations. Here, we describe the temporary ectopic implantation and subsequent replantation of a partially amputated hand and highlight the "Three R's" - Recovery, Rehabilitation, and Revision over the first year of recovery.
Keywords: Hand replantation; digit replantation; microsurgery.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare(s) that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ectopic Banking and Implantation of an Amputated Hand.Indian J Orthop. 2020 Mar 18;54(5):731-737. doi: 10.1007/s43465-020-00078-7. eCollection 2020 Sep. Indian J Orthop. 2020. PMID: 32843952 Free PMC article.
-
Revascularization and Replantation in the Hand: Ectopic Banking and Replantation.Hand Clin. 2019 May;35(2):199-206. doi: 10.1016/j.hcl.2019.01.002. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Hand Clin. 2019. PMID: 30928051 Review.
-
Salvage of Devascularized and Amputated Upper Extremity Digits with Temporary Ectopic Replantation: Our Clinical Series.J Invest Surg. 2022 Jul;35(7):1451-1461. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2022.2062497. Epub 2022 Apr 12. J Invest Surg. 2022. PMID: 35414330
-
Salvage of amputated upper extremities with temporary ectopic implantation followed by replantation at a second stage.J Reconstr Microsurg. 2006 Jan;22(1):15-20. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-931901. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2006. PMID: 16425116
-
Temporary ectopic implantation for salvaging amputated parts: A systematic review.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018 Jun;84(6):985-993. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001817. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018. PMID: 29370061
Cited by
-
Temporary ectopic banking as a treatment option for mangled thumb: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2025 Jan 25;19(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13256-025-05058-9. J Med Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39863882 Free PMC article.
-
Brief Ectopic Banking and Immediate Plate Fixation With Free Omental Flap Addresses Multiple Fundamental Problems for Single-Stage Replant of Transhumeral Amputation.Hand (N Y). 2025 Jan 30:15589447251314143. doi: 10.1177/15589447251314143. Online ahead of print. Hand (N Y). 2025. PMID: 39882745 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
