The effects of parent-child separation on the digital literacy of children and adolescents: A bidirectional perspective study
- PMID: 38778964
- PMCID: PMC11108987
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31113
The effects of parent-child separation on the digital literacy of children and adolescents: A bidirectional perspective study
Abstract
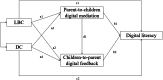
From a bidirectional perspective, the present cross-sectional study explored the impacts of parent-child separation on the digital literacy of children and adolescents. Drawing upon data from 1894 students (12-18 years, 49.33 % females) in Nanling county, China, we found that parent-child separation can negatively affect the digital literacy of children and adolescents, but effects differ between children experiencing parental migration or parental divorce. Parental mediation can act as a mediator in this process while children's digital feedback to parents may be considered as an auxiliary promoter. To further promote the digital literacy of children and adolescents experiencing parent-child separation, assigned tasks from adults in which children can practice knowledge and skills related to digital devices and the Internet are recommended.
Keywords: 21st century abilities; Informal learning; Information literacy; Mobile learning.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Roberts James A., David Meredith E. My life has become a major distraction from my cell phone: Partner phubbing and relationship satisfaction among romantic partners. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016;54:134–141.
-
- Siddiq F., Hatlevik O.E., Olsen R.V., et al. Taking a future perspective by learning from the past - a systematic review of assessment instruments that aim to measure primary and secondary school students' ICT literacy. Educ. Res. Rev. 2016;19:58–84. doi: 10.1016/j.edurev.2016.05.002. - DOI
-
- Binkley M., Erstad O., Herman J., et al. In: Defining Twenty-First Century Skills. Griffin P., McGaw B., Care E., editors. 2012.
-
- Care E., Luo R. United Nations Education, Scientific and Cultural Organization; 2016. Assessment of Transversal Competencies: Policy and Practice in the Asia-Pacific Region.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources