Analyzing the involvement of diverse cell death-related genes in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using bioinformatics techniques
- PMID: 38779021
- PMCID: PMC11108851
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30831
Analyzing the involvement of diverse cell death-related genes in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using bioinformatics techniques
Abstract
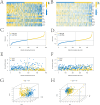
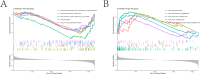
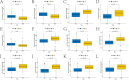
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) stands as the most prevalent subtype of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and exhibits significant heterogeneity. Various forms of programmed cell death (PCD) have been established to have close associations with tumor onset and progression. To this end, this study has compiled 16 PCD-related genes. The investigation delved into genes linked with prognosis, constructing risk models through consecutive application of univariate Cox regression analysis and Lasso-Cox regression analysis. Furthermore, we employed RT-qPCR to validate the mRNA expression levels of certain diagnosis-related genes. Subsequently, the models underwent validation through KM survival curves and ROC curves, respectively. Additionally, nomogram models were formulated employing prognosis-related genes and risk scores. Lastly, disparities in immune cell infiltration abundance and the expression of immune checkpoint-associated genes between high- and low-risk groups, as classified by risk models, were explored. These findings contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the role played by the 16 PCD-associated genes in DLBCL, shedding light on potential novel therapeutic strategies for the condition.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma; Prognosis; Programmed cell death; Risk model.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








References
-
- Dawiec P., et al. Automatic subtyping of Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphomas (DLBCL): Raman-based genetic and metabolic classification. Spectrochim. Acta Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024;309 - PubMed
-
- Poletto S., et al. Treatment strategies for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 2022;110 - PubMed
-
- Ennishi D., et al. Toward a new molecular taxonomy of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2020;10(9):1267–1281. - PubMed
-
- Zou Y., et al. Leveraging diverse cell-death patterns to predict the prognosis and drug sensitivity of triple-negative breast cancer patients after surgery. Int. J. Surg. 2022;107 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

