Leveraging radiomics and AI for precision diagnosis and prognostication of liver malignancies
- PMID: 38779098
- PMCID: PMC11109422
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1362737
Leveraging radiomics and AI for precision diagnosis and prognostication of liver malignancies
Abstract
Liver tumors, whether primary or metastatic, have emerged as a growing concern with substantial global health implications. Timely identification and characterization of liver tumors are pivotal factors in order to provide optimum treatment. Imaging is a crucial part of the detection of liver tumors; however, conventional imaging has shortcomings in the proper characterization of these tumors which leads to the need for tissue biopsy. Artificial intelligence (AI) and radiomics have recently emerged as investigational opportunities with the potential to enhance the detection and characterization of liver lesions. These advancements offer opportunities for better diagnostic accuracy, prognostication, and thereby improving patient care. In particular, these techniques have the potential to predict the histopathology, genotype, and immunophenotype of tumors based on imaging data, hence providing guidance for personalized treatment of such tumors. In this review, we outline the progression and potential of AI in the field of liver oncology imaging, specifically emphasizing manual radiomic techniques and deep learning-based representations. We discuss how these tools can aid in clinical decision-making challenges. These challenges encompass a broad range of tasks, from prognosticating patient outcomes, differentiating benign treatment-related factors and actual disease progression, recognizing uncommon response patterns, and even predicting the genetic and molecular characteristics of the tumors. Lastly, we discuss the pitfalls, technical limitations and future direction of these AI-based techniques.
Keywords: AI; HCC; liver tumors; radiomics; review.
Copyright © 2024 Haghshomar, Rodrigues, Kalyan, Velichko and Borhani.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
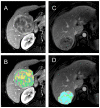
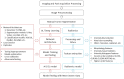
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

