Does losing reduce the tendency to engage with rivals to reach mates? An experimental test
- PMID: 38779595
- PMCID: PMC11107846
- DOI: 10.1093/beheco/arae037
Does losing reduce the tendency to engage with rivals to reach mates? An experimental test
Abstract
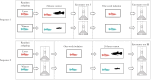
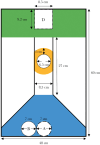
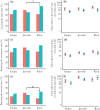
Male-male contests for access to females or breeding resources are critical in determining male reproductive success. Larger males and those with more effective weaponry are more likely to win fights. However, even after controlling for such predictors of fighting ability, studies have reported a winner-loser effect: previous winners are more likely to win subsequent contests, while losers often suffer repeated defeats. While the effect of winning-losing is well-documented for the outcome of future fights, its effect on other behaviors (e.g. mating) remains poorly investigated. Here, we test whether a winning versus losing experience influenced subsequent behaviors of male mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) toward rivals and potential mates. We housed focal males with either a smaller or larger opponent for 24 h to manipulate their fighting experience to become winners or losers, respectively. The focal males then underwent tests that required them to enter and swim through a narrow corridor to reach females, bypassing a cylinder that contained either a larger rival male (competitive scenario), a juvenile or was empty (non-competitive scenarios). The tests were repeated after 1 wk. Winners were more likely to leave the start area and to reach the females, but only when a larger rival was presented, indicating higher levels of risk-taking behavior in aggressive interactions. This winner-loser effect persisted for at least 1 wk. We suggest that male mosquitofish adjust their assessment of their own and/or their rival's fighting ability following contests in ways whose detection by researchers depends on the social context.
Keywords: contests; male–male competition; mosquitofish; sexual selection; winner–loser effect.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Society for Behavioral Ecology.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no competing interests.
Figures
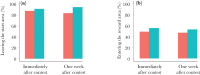
References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magalhães PJ, Ram SJ.. 2004. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 11(7):36–42. https://dspace.library.uu.nl/handle/1874/204900
-
- Allen ML, Krofel M.. 2017. Resource holding potential. In: Vonk J, Shackelford T, editors. Encyclopedia of Animal Cognition and Behavior. Cham: Springer International Publishing. p. 1–3.
-
- Arak A. 1983. Sexual selection by male–male competition in natterjack toad choruses. Nature. 306(5940):261–262. 10.1038/306261a0 - DOI
-
- Ariyomo TO, Watt PJ.. 2012. The effect of variation in boldness and aggressiveness on the reproductive success of zebrafish. Anim Behav. 83(1):41–46. 10.1016/j.anbehav.2011.10.004 - DOI
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

