Isolation and characterization of Hc-targeting chimeric heavy chain antibodies neutralizing botulinum neurotoxin type B
- PMID: 38779676
- PMCID: PMC11109933
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1380694
Isolation and characterization of Hc-targeting chimeric heavy chain antibodies neutralizing botulinum neurotoxin type B
Abstract
Background: Botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) produced by Clostridium botulinum is one of the most potent known toxins. Moreover, BoNT is classified as one of the most important biological warfare agents that threatens the biosafety of the world. Currently, the approved treatment for botulism in humans is the use of polyvalent horse serum antitoxins. However, they are greatly limited because of insufficient supply and adverse reactions. Thus, treatment of human botulism requires the development of effective toxin-neutralizing antibodies. Considering their advantages, neutralizing nanobodies will play an increasing role as BoNTs therapeutics.
Methods: Herein, neutralizing nanobodies binding to the heavy chain (Hc) domain of BoNT/B (BHc) were screened from a phage display library. Then, BoNT/B-specific clones were identified and fused with the human Fc fragment (hFc) to form chimeric heavy chain antibodies. Finally, the affinity, specificity, and neutralizing activity of antibodies against BoNT/B in vivo were evaluated.
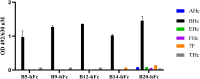
Results: The B5-hFc, B9-hFc and B12-hFc antibodies demonstrated high affinity for BHc in the nanomolar range. The three antibodies were proven to have potent neutralizing activity against BoNT/B in vivo.
Conclusion: The results demonstrate that inhibiting toxin binding to the host receptor is an efficient strategy and the three antibodies could be used as candidates for the further development of drugs to prevent and treat botulism.
Keywords: Hc domain; botulinum neurotoxin type B; heavy chain antibody; nanobody; neutralizing antibody; phage display library.
Copyright © 2024 Jiang, Wang, Guo, Cheng, Chen, Wang, Li, Du, Gao, Lu, Yu and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Maslanka SE, Luquez C, Dykes JK, Tepp WH, Pier CL, Pellett S, et al. . A novel botulinum neurotoxin, previously reported as serotype H, has a hybrid-like structure with regions of similarity to the structures of serotypes A and F and is neutralized with serotype A antitoxin. J Infect Dis. (2016) 213:379–85. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv327 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

