Novel horizons in anticoagulation: the emerging role of factor XI inhibitors across different settings
- PMID: 38779744
- PMCID: PMC11443408
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2023.283682
Novel horizons in anticoagulation: the emerging role of factor XI inhibitors across different settings
Abstract
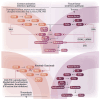
Anticoagulants have long been fundamental in preventing and treating thromboembolic disorders, with a recent shift of focus towards direct oral anticoagulants, thanks to their ease of use, efficacy, and safety. Despite these advancements, bleeding complications remain a major concern with any anticoagulant, highlighting the need for safer drugs. Factor XI (FXI) inhibitors have emerged as promising agents in this regard, offering a novel approach by targeting upstream factors in the coagulation system. Phase II trials have shown encouraging outcomes, indicating a reduced bleeding risk compared to that associated with traditional anticoagulants, particularly in the context of cardiovascular disease management when combined with antiplatelet therapy. However, the variability in findings and limited efficacy data call for a cautious interpretation pending insights from phase III trials. These trials are essential for validating the potential of FXI inhibitors to balance bleeding risk reduction and maintain anticoagulant efficacy. This review explores the pharmacology, potential indications, clinical data, and future directions of FXI inhibitors, providing a perspective on their evolving role in anticoagulant therapy. It also provides a detailed analysis of data from published clinical trials on FXI inhibitors in various indications. Preliminary data from ongoing trials are also outlined. As the field moves forward, a cautiously optimistic outlook can be expected, focusing on comprehensive data from phase III trials to define the role of FXI inhibitors in various clinical scenarios.
Figures
References
-
- Carnicelli AP, Hong H, Connolly SJ, et al. ; COMBINE AF. Direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: patient-level network meta-analyses of randomized clinical trials with interaction testing by age and sex. Circulation. 2022;145(4):242-255. Erratum in: Circulation. 2022;145(8): e640. - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Es N, Coppens M, Schulman S, Middeldorp S, Büller HR. Direct oral anticoagulants compared with vitamin K antagonists for acute venous thromboembolism: evidence from phase 3 trials. Blood. 2014;124(12):1968-1975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

