Mitochondrial DNA release and sensing in innate immune responses
- PMID: 38779772
- PMCID: PMC11112387
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddae031
Mitochondrial DNA release and sensing in innate immune responses
Abstract
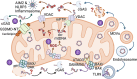
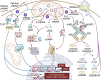
Mitochondria are pleiotropic organelles central to an array of cellular pathways including metabolism, signal transduction, and programmed cell death. Mitochondria are also key drivers of mammalian immune responses, functioning as scaffolds for innate immune signaling, governing metabolic switches required for immune cell activation, and releasing agonists that promote inflammation. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is a potent immunostimulatory agonist, triggering pro-inflammatory and type I interferon responses in a host of mammalian cell types. Here we review recent advances in how mtDNA is detected by nucleic acid sensors of the innate immune system upon release into the cytoplasm and extracellular space. We also discuss how the interplay between mtDNA release and sensing impacts cellular innate immune endpoints relevant to health and disease.
Keywords: NLRP3; TLR9; cGAS-STING; inflammation; innate immunity; mitochondria; mitochondrial DNA.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Mills EL, Kelly B, O'Neill LAJ. Mitochondria are the powerhouses of immunity. Nat Immunol 2017;18:488–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- W81XWH-20-1-0150/Office of the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Health Affairs through the Peer Reviewed Medical Research Programs
- F31 AI179168/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL148153/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148153/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RGPIN-2016-04083/Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

