Pathologic TDP-43 downregulates myelin gene expression in the monkey brain
- PMID: 38779803
- PMCID: PMC11483520
- DOI: 10.1111/bpa.13277
Pathologic TDP-43 downregulates myelin gene expression in the monkey brain
Abstract
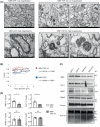
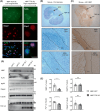
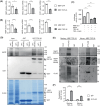
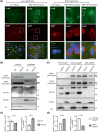
Growing evidence indicates that non-neuronal oligodendrocyte plays an important role in Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and other neurodegenerative diseases. In patient's brain, the impaired myelin structure is a pathological feature with the observation of TDP-43 in cytoplasm of oligodendrocyte. However, the mechanism underlying the gain of function by TDP-43 in oligodendrocytes, which are vital for the axonal integrity, remains unclear. Recently, we found that the primate-specific cleavage of truncated TDP-43 fragments occurred in cytoplasm of monkey neural cells. This finding opened up the avenue to investigate the myelin integrity affected by pathogenic TDP-43 in oligodendrocytes. In current study, we demonstrated that the truncated TDP-35 in oligodendrocytes specifically, could lead to the dysfunctional demyelination in corpus callosum of monkey. As a consequence of the interaction of myelin regulatory factor with the accumulated TDP-35 in cytoplasm, the downstream myelin-associated genes expression was downregulated at the transcriptional level. Our study aims to investigate the potential effect on myelin structure injury, affected by the truncated TDP-43 in oligodendrocyte, which provided the additional clues on the gain of function during the progressive pathogenesis and symptoms in TDP-43 related diseases.
Keywords: MyRF; TDP‐43; myelination; non‐human primate; oligodendrocytes.
© 2024 The Author(s). Brain Pathology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International Society of Neuropathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ALS-linked mutant TDP-43 in oligodendrocytes induces oligodendrocyte damage and exacerbates motor dysfunction in mice.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024 Nov 27;12(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s40478-024-01893-x. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024. PMID: 39605053 Free PMC article.
-
Demyelination and impaired oligodendrogenesis in the corpus callosum following lead exposure.Toxicol Sci. 2024 Nov 1;202(1):123-141. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfae100. Toxicol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39150886 Free PMC article.
-
Single intracerebroventricular TNFR2 agonist injection impacts remyelination in the cuprizone model.J Mol Med (Berl). 2025 Jul;103(7):795-807. doi: 10.1007/s00109-025-02549-6. Epub 2025 May 10. J Mol Med (Berl). 2025. PMID: 40347238 Free PMC article.
-
Uncommon Non-MS Demyelinating Disorders of the Central Nervous System.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):45. doi: 10.1007/s11910-025-01432-8. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40591029 Review.
-
A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Early Life Stress on the Prefrontal Cortex Transcriptome Reveals Long-Term Downregulation of Myelin-Related Gene Expression.Brain Behav. 2025 Jun;15(6):e70608. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70608. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40524640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Schwann Cells in Neuromuscular Disorders: A Spotlight on Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Cells. 2025 Jan 3;14(1):47. doi: 10.3390/cells14010047. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39791748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progranulin deficiency does not exacerbate TDP-43 pathology in TDP-43 transgenic mouse models.NPJ Dement. 2025;1(1):16. doi: 10.1038/s44400-025-00020-4. Epub 2025 Jul 21. NPJ Dement. 2025. PMID: 40703981 Free PMC article.
-
White matter pathology in FTLD caused by GRN mutations.Acta Neuropathol. 2025 Jan 15;149(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s00401-025-02847-w. Acta Neuropathol. 2025. PMID: 39812821 No abstract available.
References
-
- Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT, et al. Ubiquitinated TDP‐43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science. 2006;314(5796):130–133. - PubMed
-
- Kwong LK, Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Lee VM‐Y, Trojanowski JQ. TDP‐43 proteinopathy: the neuropathology underlying major forms of sporadic and familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration and motor neuron disease. Acta Theriol Neuropathol. 2007;114:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Neumann M, Kwong LK, Sampathu DM, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM‐Y. TDP‐43 proteinopathy in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: protein misfolding diseases without amyloidosis. Arch Neurol. 2007;64(10):1388–1394. - PubMed
-
- Buratti E. Functional significance of TDP‐43 mutations in disease. Adv Genet. 2015;91:1–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

