CD200R activation on naïve T cells by B cells induces suppressive activity of T cells via IL-24
- PMID: 38780647
- PMCID: PMC11116298
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-024-05268-2
CD200R activation on naïve T cells by B cells induces suppressive activity of T cells via IL-24
Abstract
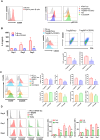
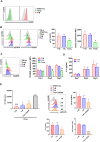
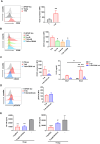
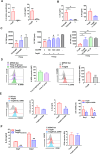
CD200 is an anti-inflammatory protein that facilitates signal transduction through its receptor, CD200R, in cells, resulting in immune response suppression. This includes reducing M1-like macrophages, enhancing M2-like macrophages, inhibiting NK cell cytotoxicity, and downregulating CTL responses. Activation of CD200R has been found to modulate dendritic cells, leading to the induction or enhancement of Treg cells expressing Foxp3. However, the precise mechanisms behind this process are still unclear. Our previous study demonstrated that B cells in Peyer's patches can induce Treg cells, so-called Treg-of-B (P) cells, through STAT6 phosphorylation. This study aimed to investigate the role of CD200 in Treg-of-B (P) cell generation. To clarify the mechanisms, we used wild-type, STAT6 deficient, and IL-24 deficient T cells to generate Treg-of-B (P) cells, and antagonist antibodies (anti-CD200 and anti-IL-20RB), an agonist anti-CD200R antibody, CD39 inhibitors (ARL67156 and POM-1), a STAT6 inhibitor (AS1517499), and soluble IL-20RB were also applied. Our findings revealed that Peyer's patch B cells expressed CD200 to activate the CD200R on T cells and initiate the process of Treg-of-B (P) cells generation. CD200 and CD200R interaction triggers the phosphorylation of STAT6, which regulated the expression of CD200R, CD39, and IL-24 in T cells. CD39 regulated the expression of IL-24, which sustained the expression of CD223 and IL-10 and maintained the cell viability. In summary, the generation of Treg-of-B (P) cells by Peyer's patch B cells was through the CD200R-STAT6-CD39-IL-24 axis pathway.
Keywords: B cells; CD200; IL-24; Peyer’s patch; Treg cell.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Gorczynski R, Khatri I, Lee L, Boudakov I. An Interaction between CD200 and monoclonal antibody agonists to CD200R2 in development of dendritic cells that preferentially induce populations of CD4 + CD25 + T Regulatory cells. J Immunol. 2008;180(9):5946–5955. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.9.5946. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

