ESR Essentials: using the right scoring system in prostate MRI-practice recommendations by ESUR
- PMID: 38780764
- PMCID: PMC11519295
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-024-10792-7
ESR Essentials: using the right scoring system in prostate MRI-practice recommendations by ESUR
Abstract
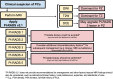
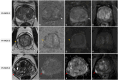
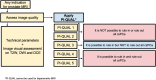
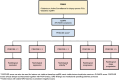
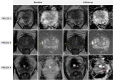
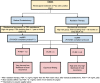
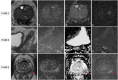
MRI has gained prominence in the diagnostic workup of prostate cancer (PCa) patients, with the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) being widely used for cancer detection. Beyond PI-RADS, other MRI-based scoring tools have emerged to address broader aspects within the PCa domain. However, the multitude of available MRI-based grading systems has led to inconsistencies in their application within clinical workflows. The Prostate Cancer Radiological Estimation of Change in Sequential Evaluation (PRECISE) assesses the likelihood of clinically significant radiological changes of PCa during active surveillance, and the Prostate Imaging for Local Recurrence Reporting (PI-RR) scoring system evaluates the risk of local recurrence after whole-gland therapies with curative intent. Underlying any system is the requirement to assess image quality using the Prostate Imaging Quality Scoring System (PI-QUAL). This article offers practicing radiologists a comprehensive overview of currently available scoring systems with clinical evidence supporting their use for managing PCa patients to enhance consistency in interpretation and facilitate effective communication with referring clinicians. KEY POINTS: Assessing image quality is essential for all prostate MRI interpretations and the PI-QUAL score represents the standardized tool for this purpose. Current urological clinical guidelines for prostate cancer diagnosis and localization recommend adhering to the PI-RADS recommendations. The PRECISE and PI-RR scoring systems can be used for assessing radiological changes of prostate cancer during active surveillance and the likelihood of local recurrence after radical treatments respectively.
Keywords: Classification; management; Magnetic resonance imaging; Prostate cancer; Standardization.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Andrea Ponsiglione holds the position of Junior Deputy Editor at European Radiology and is a member of the Scientific Editorial Board of Insights into Imaging, but he has not taken part in the review or selection process of this article. Valeria Panebianco is member of the European Radiology Scientific Editorial Board. She has not taken part in the review or selection process of this article. Renato Cuocolo is member of the European Radiology Scientific Editorial Board. He has not taken part in the review or selection process of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Padhani AR, Schoots IG (2023) Imaging-based diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for prostate cancer in the coming decades. Radiology 307:e222990. 10.1148/radiol.222990 - PubMed
-
- Turkbey B, Rosenkrantz AB, Haider MA et al (2019) Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System version 2.1: 2019 update of prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2. Eur Urol. 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.02.033 - PubMed
-
- Giganti F, Allen C, Emberton M et al (2020) Prostate Imaging Quality (PI-QUAL): a new quality control scoring system for multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate from the Precision trial. Eur Urol Oncol 3:615–619. 10.1016/j.euo.2020.06.007 - PubMed
-
- Moore CM, Giganti F, Albertsen P et al (2017) Reporting magnetic resonance imaging in men on active surveillance for prostate cancer: the PRECISE recommendations—a report of a European School of Oncology Task Force. Eur Urol 71:648–655. 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.011 - PubMed
-
- Panebianco V, Villeirs G, Weinreb JC et al (2021) Prostate magnetic resonance imaging for local recurrence reporting (PI-RR): international consensus -based guidelines on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for prostate cancer recurrence after radiation therapy and radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol Oncol 4:868–876. 10.1016/j.euo.2021.01.003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

