Monkeypox Virus Infections After 2 Preexposure Doses of JYNNEOS Vaccine - United States, May 2022-May 2024
- PMID: 38781111
- PMCID: PMC11115437
- DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7320a3
Monkeypox Virus Infections After 2 Preexposure Doses of JYNNEOS Vaccine - United States, May 2022-May 2024
Abstract
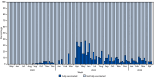
Two doses of JYNNEOS vaccine are effective in preventing many mpox cases and can reduce the severity of symptoms in infected persons. However, infections among fully vaccinated persons can occur. During May 2022-May 2024, a total of 271 mpox cases among fully vaccinated persons were reported to CDC from 27 U.S. jurisdictions. These reported infections are estimated to have occurred in <1% of fully vaccinated persons. Compared with cases among unvaccinated persons, infections among fully vaccinated persons were more likely to occur among non-Hispanic White men aged 30-39 years, were associated with increased numbers of sexual partners, and resulted in less severe disease (p<0.001). Among infections in fully vaccinated persons with complete data, infections after vaccination were reported more commonly after receipt of heterologous (subcutaneous and intradermal) (46%) or homologous subcutaneous (32%) JYNNEOS vaccination than after homologous intradermal (22%) vaccination. Disparate time intervals from vaccination to infection among fully vaccinated persons suggest that immunity is not waning. The median interval between the second vaccine dose and illness onset was longer for cases among persons who had received 2 intradermal doses (median = 363 days; IQR = 221-444 days) compared with cases in persons who had received 2 subcutaneous doses (median = 263 days; IQR = 47-334 days) (p<0.001). The implications of this finding are not known; however, these data should increase confidence in the effectiveness of vaccine doses that were administered intradermally, the preferred method of administration during the peak of the outbreak when vaccine supply was limited. Persons recommended to receive the JYNNEOS vaccine should receive 2 doses, irrespective of the route of administration, and at this time, additional doses are not recommended for the affected population.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed and submitted the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors form for disclosure of potential conflicts of interest. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Dalton AF, Diallo AO, Chard AN, et al. ; CDC Multijurisdictional Mpox Case Control Study Group. Estimated effectiveness of JYNNEOS vaccine in preventing mpox: a multijurisdictional case-control study—United States, August 19, 2022–March 31, 2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2023;72:553–8. 10.15585/mmwr.mm7220a3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

