Dynamic analysis and optimal control of stochastic information cross-dissemination and variation model with random parametric perturbations
- PMID: 38781238
- PMCID: PMC11115323
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303300
Dynamic analysis and optimal control of stochastic information cross-dissemination and variation model with random parametric perturbations
Abstract
Information dissemination has a significant impact on social development. This paper considers that there are many stochastic factors in the social system, which will result in the phenomena of information cross-dissemination and variation. The dual-system stochastic susceptible-infectious-mutant-recovered model of information cross-dissemination and variation is derived from this problem. Afterward, the existence of the global positive solution is demonstrated, sufficient conditions for the disappearance of information and its stationary distribution are calculated, and the optimal control strategy for the stochastic model is proposed. The numerical simulation supports the results of the theoretical analysis and is compared to the parameter variation of the deterministic model. The results demonstrate that cross-dissemination of information can result in information variation and diffusion. Meanwhile, white noise has a positive effect on information dissemination, which can be improved by adjusting the perturbation parameters.
Copyright: © 2024 Kang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





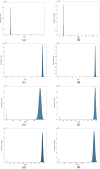



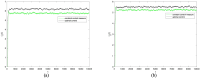
References
-
- Hu Y, Liu H, Zhao J, Tu L. Dynamic analysis of dissemination model of innovation ability of enterprise R&D personnel. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications. 2019;531:121743. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.121743 - DOI
-
- Vargo SL, Akaka MA, Wieland H. Rethinking the process of diffusion in innovation: A service-ecosystems and institutional perspective. Journal of Business Research. 2020;116:526–534. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.01.038 - DOI
-
- Yang X, Jiang H, Yu Z. Global dynamics of ILSR rumor spreading model with general nonlinear spreading rate in multi-lingual environment. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals. 2022;154:111698. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2021.111698 - DOI
-
- Cheng Y, Huo L, Zhao L. Stability analysis and optimal control of rumor spreading model under media coverage considering time delay and pulse vaccination. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals. 2022;157:111931. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2022.111931 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

