Nobiletin regulates intracellular Ca2+ levels via IP3R and ameliorates neuroinflammation in Aβ42-induced astrocytes
- PMID: 38781730
- PMCID: PMC11145555
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103197
Nobiletin regulates intracellular Ca2+ levels via IP3R and ameliorates neuroinflammation in Aβ42-induced astrocytes
Abstract
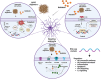
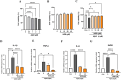
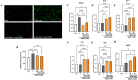
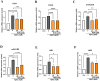
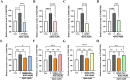
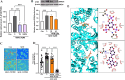
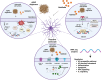
Astrocytes are the major glial cells in the human brain and provide crucial metabolic and trophic support to neurons. The amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) alter the morphological and functional properties of astrocytes and induce inflammation and calcium dysregulation, contributing to Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology. Recent studies highlight the role of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4/nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling in inflammation. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated due to Aβ, induce apoptosis in the brain cells worsening AD progression. Astrocytic cell surface receptors, such as purinergic receptors (P2Y1 and P2Y2), metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGLUR)5, α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR), and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs), have been suggested to interact with inositol trisphosphate receptor (IP3R) on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to induce Ca2+ movement from ER to cytoplasm, causing Ca2+ dysregulation. We found that the citrus flavonoid nobiletin (NOB) protected primary astrocytes from Aβ42-induced cytotoxicity and inhibited TLR4/NF-κB signaling in Aβ42-induced primary rat astrocytes. NOB was found to regulate Aβ42-induced ROS levels through Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. The receptors P2Y1, P2Y2, mGLUR5, α7nAChR, and NMDARs induced intracellular Ca2+ levels by activating IP3R and NOB regulated them, thereby regulating intracellular Ca2+ levels. Molecular docking analysis revealed a possible interaction between NOB and IP3R in IP3R regulation. Furthermore, RNA sequencing revealed various NOB-mediated biological signaling pathways, such as the AD-presenilin, AD-amyloid secretase, and Wnt signaling pathway, suggesting possible neuroprotective roles of NOB. To conclude, NOB is a promising therapeutic agent for AD and works by modulating AD pathology at various levels in Aβ42-induced primary rat astrocytes.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Calcium dysregulation; Citrus flavonoid; Neuroinflammation; Nobiletin.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Murphy M.P., LeVine H. 3rd, Alzheimer's disease and the amyloid-beta peptide. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;19(1):311–323. - PubMed
-
- Herculano‐Houzel S. The glia/neuron ratio: how it varies uniformly across brain structures and species and what that means for brain physiology and evolution. Glia. 2014;62(9):1377–1391. - PubMed
-
- Devaraju P., Sun M.-Y., Myers T.L., Lauderdale K., Fiacco T.A. Astrocytic group I mGluR-dependent potentiation of astrocytic glutamate and potassium uptake. J. Neurophysiol. 2013;109(9):2404–2414. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

