Severe Bottleneck Impacted the Genomic Structure of Egg-Eating Cichlids in Lake Victoria
- PMID: 38782570
- PMCID: PMC11166178
- DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msae093
Severe Bottleneck Impacted the Genomic Structure of Egg-Eating Cichlids in Lake Victoria
Abstract
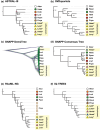
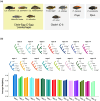
Within 15,000 years, the explosive adaptive radiation of haplochromine cichlids in Lake Victoria, East Africa, generated 500 endemic species. In the 1980s, the upsurge of Nile perch, a carnivorous fish artificially introduced to the lake, drove the extinction of more than 200 endemic cichlids. The Nile perch predation particularly harmed piscivorous cichlids, including paedophages, cichlids eat eggs and fries, which is an example of the unique trophic adaptation seen in African cichlids. Here, aiming to investigate past demographic events possibly triggered by the invasion of Nile perch and the subsequent impacts on the genetic structure of cichlids, we conducted large-scale comparative genomics. We discovered evidence of recent bottleneck events in 4 species, including 2 paedophages, which began during the 1970s to 1980s, and population size rebounded during the 1990s to 2000s. The timing of the bottleneck corresponded to the historical records of endemic haplochromines" disappearance and later resurgence, which is likely associated with the introduction of Nile perch by commercial demand to Lake Victoria in the 1950s. Interestingly, among the 4 species that likely experienced bottleneck, Haplochromis sp. "matumbi hunter," a paedophagous cichlid, showed the most severe bottleneck signatures. The components of shared ancestry inferred by ADMIXTURE suggested a high genetic differentiation between matumbi hunter and other species. In contrast, our phylogenetic analyses highly supported the monophyly of the 5 paedophages, consistent with the results of previous studies. We conclude that high genetic differentiation of matumbi hunter occurred due to the loss of shared genetic components among haplochromines in Lake Victoria caused by the recent severe bottleneck.
Keywords: bottleneck; cichlid; genetic diversity; genetic structure; paedophage.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Pleistocene desiccation in East Africa bottlenecked but did not extirpate the adaptive radiation of Lake Victoria haplochromine cichlid fishes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Aug 11;106(32):13404-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902299106. Epub 2009 Jul 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19651614 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Signatures for Species-Specific Adaptation in Lake Victoria Cichlids Derived from Large-Scale Standing Genetic Variation.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 Jul 29;38(8):3111-3125. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab084. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33744961 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia Tolerance in Twelve Species of East African Cichlids: Potential for Low Oxygen Refugia in Lake Victoria.Conserv Biol. 1995 Oct;9(5):1274-1288. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1739.1995.9051262.x-i1. Conserv Biol. 1995. PMID: 34261244
-
The species flocks of East African cichlid fishes: recent advances in molecular phylogenetics and population genetics.Naturwissenschaften. 2004 Jun;91(6):277-90. doi: 10.1007/s00114-004-0528-6. Epub 2004 Apr 20. Naturwissenschaften. 2004. PMID: 15241604 Review.
-
The diversity of male nuptial coloration leads to species diversity in Lake Victoria cichlids.Genes Genet Syst. 2013;88(3):145-53. doi: 10.1266/ggs.88.145. Genes Genet Syst. 2013. PMID: 24025243 Review.
Cited by
-
Archaeogenomic insights into commensalism and regional variation in pig management in Neolithic northwest Europe.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Mar 25;122(12):e2410235122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2410235122. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40096601
References
-
- Andrews S. FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. 2010. http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/.
-
- Bouckaert R, Heled J. DensiTree 2: seeing trees through the forest. bioRxiv. 2014. 10.1101/012401. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

