Causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and bronchiectasis: a bidirectional mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 38783321
- PMCID: PMC11112812
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-024-03336-3
Causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and bronchiectasis: a bidirectional mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Background: Epidemiological observational studies have elucidated a correlation between rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and bronchiectasis. However, the causal nature of this association remains ambiguous. To clarify this potential causal linkage, we conducted a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis to explore the bidirectional causality between RA and bronchiectasis.
Methods: Summary statistics for RA and bronchiectasis were obtained from the IEU OpenGWAS database We employed various methods, including inverse variance weighting (IVW), MR-Egger, weighted median, weighted mode, and simple mode, to explore potential causal links between RA and bronchiectasis. Additionally, a series of sensitivity studies, such as Cochran's Q test, MR Egger intercept test, and leave-one-out analysis, were conducted to assess the MR analysis's accuracy further.
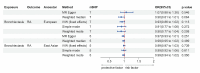
Results: In the forward MR analysis, the primary analysis indicated that a genetic predisposition to RA correlated with an increased risk of bronchiectasis in European populations (IVW odds ratio (OR): 1.28, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.20-1.37, p = 1.18E-13). Comparable results were noted in the East Asian subjects (IVW OR: 1.55, 95% CI: 1.30-1.34, p = 8.33E-07). The OR estimates from the other four methods were consistent with those obtained from the IVW method. Sensitivity analysis detected no evidence of horizontal pleiotropy or heterogeneity. Conversely, in the reverse MR analysis, we found no evidence to support a genetic causality between bronchiectasis and RA in either European or East Asian populations.
Conclusion: This study indicates that genetic predisposition to RA correlates with a heightened risk of bronchiectasis in both European and East Asian populations. These results imply that routine screening for bronchiectasis in RA patients could be beneficial, and effective management of RA may contribute to a reduced risk of bronchiectasis. Future research should aim to clarify the underlying mechanisms linking these two conditions.
Keywords: Bronchiectasis; Genome-wide association study; Mendelian randomization; Rheumatoid arthritis; Single-nucleotide polymorphisms.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Causal associations of air pollution with rheumatoid arthritis: A transethnic Mendelian randomization study.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 24;19(9):e0307514. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307514. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39316602 Free PMC article.
-
Causal associations between rheumatoid arthritis, cataract and glaucoma in European and East Asian populations: A bidirectional two-sample mendelian randomization study.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 4;19(3):e0299192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299192. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38437213 Free PMC article.
-
The Association between Rheumatic Diseases and the Risk of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis.Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2024 Nov 30;85(11):1-19. doi: 10.12968/hmed.2024.0478. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39618216
-
Analysis of the causal relationship between immune cells and rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of genetic variation: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Adv Rheumatol. 2024 Nov 1;64(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s42358-024-00425-4. Adv Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39487558 Review.
-
Genetic relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular diseases : A systematic review of Mendelian randomization studies.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2025 May;137(9-10):272-278. doi: 10.1007/s00508-024-02392-8. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2025. PMID: 39060548 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Genetic Association Between Connective Tissue Diseases and the Risk of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis.Pulm Circ. 2024 Dec 24;14(4):e70033. doi: 10.1002/pul2.70033. eCollection 2024 Oct. Pulm Circ. 2024. PMID: 39720342 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the genetic association between rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jan;44(1):153-160. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07258-y. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39638962
References
-
- Finckh A, Gilbert B, Hodkinson B, Bae S-C, Thomas R, Deane KD, et al. Global epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(10):591–602. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical