Near vision in patients with DME and RVO treated with aflibercept and correlation with NEI VFQ-25 questionnaire
- PMID: 38783380
- PMCID: PMC11112959
- DOI: 10.1186/s40942-024-00558-0
Near vision in patients with DME and RVO treated with aflibercept and correlation with NEI VFQ-25 questionnaire
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study is to evaluate near and distance visual acuity (VA) and their correlation with the National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire (NEI VFQ-25) outcomes in patients with diabetic macular edema (DME) and macular edema due to retinal vein occlusion (RVO) treated with aflibercept.
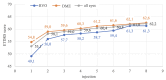
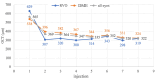
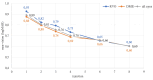
Methods: In this prospective study, we included 87 eyes of patients diagnosed with DME (n = 61) and RVO (n = 26), who received aflibercept treatment and were followed until the 8th injection. Near VA was examined on the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 6th, and 8th injection, and patients completed the NEI VFQ-25 on the 1st, 4th, and 8th aflibercept injection.
Results: The mean near VA at baseline in all eyes was 0.89 ± 0.12 logMAR. With every administration, there was a statistically significant improvement; on the 4th (0.70 ± 0.19; p = 0.000) and the 8th application (0.60 ± 0.19; p = 0.000). At baseline, the mean NEI VFQ-25 total score was 71 ± 14%, and improved to 81 ± 13% (p = 0.000) on the 8th injection. The most significant score gain was recorded in the near VA subscale (+ 20 ± 14%, p = 0.000). There was no statistically significant difference between DME and RVO group in the questionnaire or near VA outcomes.
Conclusion: Aflibercept treatment resulted in a remarkable improvement of near vision by 4 lines of logMAR optotype after the 8th application. The near vision questionnaire subscale, initially scoring the lowest, exhibited the greatest gain during the treatment period. This underscores the importance of near vision and reading ability for patients with DME and RVO.
Keywords: Aflibercept; DME; NEI VFQ-25; Near vision; RVO.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors confirm that they have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Brown DM, Schmidt-Erfurth U, Do DV, Holz FG, Boyer DS, Midena E, Heier JS, Terasaki H, Kaiser PK, Marcus DM, Nguyen QD, Jaffe GJ, Slakter JS, Simader C, Soo Y, Schmelter T, Yancopoulos GD, Stahl N, Vitti R, Berliner AJ, Zeitz O, Metzig C, Korobelnik JF. Intravitreal Aflibercept for Diabetic Macular Edema: 100-Week results from the VISTA and VIVID studies. Ophthalmology. 2015;122:2044–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.05.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Heier JS, Korobelnik JF, Brown DM, Schmidt-Erfurth U, Do DV, Midena E, Boyer DS, Terasaki H, Kaiser PK, Marcus DM, Nguyen QD, Jaffe GJ, Slakter JS, Simader C, Soo Y, Schmelter T, Vitti R, Berliner AJ, Zeitz O, Metzig C, Holz FG. Intravitreal Aflibercept for Diabetic Macular Edema: 148-Week results from the VISTA and VIVID studies. Ophthalmology. 2016;123:2376–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2016.07.032. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

