Mechanistic Insights into the Function of 14-3-3 Proteins as Negative Regulators of Brassinosteroid Signaling in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 38783418
- PMCID: PMC11558545
- DOI: 10.1093/pcp/pcae056
Mechanistic Insights into the Function of 14-3-3 Proteins as Negative Regulators of Brassinosteroid Signaling in Arabidopsis
Abstract
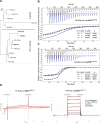
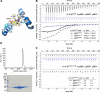
Brassinosteroids (BRs) are vital plant steroid hormones sensed at the cell surface by a membrane signaling complex comprising the receptor kinase BRI1 and a SERK family co-receptor kinase. Activation of this complex lead to dissociation of the inhibitor protein BKI1 from the receptor and to differential phosphorylation of BZR1/BES1 transcription factors by the glycogen synthase kinase 3 protein BIN2. Many phosphoproteins of the BR signaling pathway, including BRI1, SERKs, BKI1 and BZR1/BES1 can associate with 14-3-3 proteins. In this study, we use quantitative ligand binding assays to define the minimal 14-3-3 binding sites in the N-terminal lobe of the BRI1 kinase domain, in BKI1, and in BZR1 from Arabidopsis thaliana. All three motifs require to be phosphorylated to specifically bind 14-3-3s with mid- to low-micromolar affinity. BR signaling components display minimal isoform preference within the 14-3-3 non-ε subgroup. 14-3-3λ and 14-3-3 ω isoform complex crystal structures reveal that BKI1 and BZR1 bind as canonical type II 14-3-3 linear motifs. Disruption of key amino acids in the phosphopeptide binding site through mutation impairs the interaction of 14-3-3λ with all three linear motifs. Notably, quadruple loss-of-function mutants from the non-ε group exhibit gain-of-function BR signaling phenotypes, suggesting a role for 14-3-3 proteins as overall negative regulators of the BR pathway. Collectively, our work provides further mechanistic and genetic evidence for the regulatory role of 14-3-3 proteins at various stages of the BR signaling cascade.
Keywords: 14-3-3 proteins; Protein X-ray crystallography; Protein kinase; Receptor kinase; brassinosteroids; phosphopeptide.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Japanese Society of Plant Physiologists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transcription factor HAT1 is phosphorylated by BIN2 kinase and mediates brassinosteroid repressed gene expression in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2014 Jan;77(1):59-70. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12368. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Plant J. 2014. PMID: 24164091
-
Two putative BIN2 substrates are nuclear components of brassinosteroid signaling.Plant Physiol. 2002 Nov;130(3):1221-9. doi: 10.1104/pp.102.010918. Plant Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12427989 Free PMC article.
-
MYBL2 is a substrate of GSK3-like kinase BIN2 and acts as a corepressor of BES1 in brassinosteroid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Dec 4;109(49):20142-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1205232109. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23169658 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand perception, activation, and early signaling of plant steroid receptor brassinosteroid insensitive 1.J Integr Plant Biol. 2013 Dec;55(12):1198-211. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12081. Epub 2013 Sep 9. J Integr Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 23718739 Review.
-
Brassinosteroid Signaling Dynamics: Ubiquitination-Dependent Regulation of Core Signaling Components.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 8;26(10):4502. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104502. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429648 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preventing inappropriate signals pre- and post-ligand perception by a toggle switch mechanism of ERECTA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jan 28;122(4):e2420196122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2420196122. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 39841143 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

