Sample-to-answer salivary miRNA testing: New frontiers in point-of-care diagnostic technologies
- PMID: 38783564
- PMCID: PMC11141732
- DOI: 10.1002/wnan.1969
Sample-to-answer salivary miRNA testing: New frontiers in point-of-care diagnostic technologies
Abstract
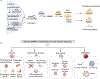
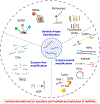
MicroRNA (miRNA), crucial non-coding RNAs, have emerged as key biomarkers in molecular diagnostics, prognosis, and personalized medicine due to their significant role in gene expression regulation. Salivary miRNA, in particular, stands out for its non-invasive collection method and ease of accessibility, offering promising avenues for the development of point-of-care diagnostics for a spectrum of diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and infectious diseases. Such development promises rapid and precise diagnosis, enabling timely treatment. Despite significant advancements in salivary miRNA-based testing, challenges persist in the quantification, multiplexing, sensitivity, and specificity, particularly for miRNA at low concentrations in complex biological mixtures. This work delves into these challenges, focusing on the development and application of salivary miRNA tests for point-of-care use. We explore the biogenesis of salivary miRNA and analyze their quantitative expression and their disease relevance in cancer, infection, and neurodegenerative disorders. We also examined recent progress in miRNA extraction, amplification, and multiplexed detection methods. This study offers a comprehensive view of the development of salivary miRNA-based point-of-care testing (POCT). Its successful advancement could revolutionize the early detection, monitoring, and management of various conditions, enhancing healthcare outcomes. This article is categorized under: Diagnostic Tools > Biosensing Diagnostic Tools > Diagnostic Nanodevices.
Keywords: cancer; infectious disease; microRNA; multiplexed detection; neurodegenerative disease; point of care testing (POCT); saliva.
© 2024 The Author(s). WIREs Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
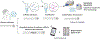
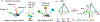



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

