New insights into the potential cardioprotective effects of telmisartan and nanoformulated extract of Spirulina platensis via regulation of oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy in an experimental model
- PMID: 38783939
- PMCID: PMC11112102
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1380057
New insights into the potential cardioprotective effects of telmisartan and nanoformulated extract of Spirulina platensis via regulation of oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy in an experimental model
Abstract
Background: Cardiotoxicity is one of the limiting side effects of the commonly used anticancer agent cyclophosphamide (Cyclo).
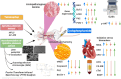
Materials and methods: The possible protective effects of telmisartan and nanoformulated Spirulina platensis (Sp) methanolic extract against Cyclo-induced cardiotoxicity were examined in this study. Experimental groups of rats were randomly divided into nine groups as control vehicle, control polymer, telmisartan (TEL, 10 mg/kg), free Sp extract (300 mg/kg), nano Sp extract (100 mg/kg), Cyclo (200 mg/kg), TEL + Cyclo, free Sp + Cyclo, and nano Sp + Cyclo. The groups with Cyclo combinations were treated in the same manner as their corresponding ones without Cyclo, with a single dose of Cyclo on day 18.
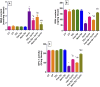
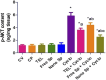
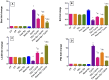
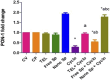
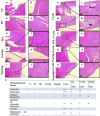
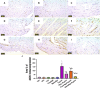
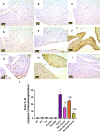
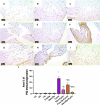
Results: The results indicate that Cyclo causes significant cardiotoxicity, manifesting in the form of notable increases of 155.49%, 105.74%, 451.76%, and 826.07% in the serum levels of glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatine kinase MB (CK-MB), and cardiac troponin I (cTnI) enzyme activities, respectively, as compared to the control. In addition, the cardiac glutathione (GSH) content and activity of glutathione peroxidase-1 (GPX-1) enzyme decreased by 65.94% and 73.85%, respectively. Treatment with nano Sp extract showed the most prominent restorations of the altered biochemical, histopathological, and immunohistochemical features as compared with those by TEL and free Sp; moreover, reductions of 30.64% and 43.02% in the p-AKT content as well as 60.43% and 75.30% of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) immunoreactivity were detected in the TEL and free Sp treatment groups, respectively. Interestingly, nano Sp boosted the autophagy signal via activation of beclin-1 (36.42% and 153.4%), activation of LC3II (69.13% and 195%), downregulation of p62 expressions (39.68% and 62.45%), and increased gene expressions of paraoxonase-1 (PON-1) (90.3% and 225.9%) compared to the TEL and free Sp treatment groups, respectively.
Conclusion: The findings suggest the protective efficiency of telmisartan and nano Sp extract against cardiotoxicity via activations of the antioxidant, antiapoptotic, and autophagy signaling pathways.
Keywords: PON-1; Spirulina platensis; autophagy; cardiotoxicity; cyclophosphamide; nanoformulation; telmisartan.
Copyright © 2024 Almukainzi, El-Masry, Ibrahim, Saad, El Zahaby, Saleh and El-Nagar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ameliorative Effect of Chitosan/Spirulina platensis Ethanolic Extract Nanoformulation against Cyclophosphamide-Induced Ovarian Toxicity: Role of PPAR-γ/Nrf-2/HO-1 and NF-kB/TNF-α Signaling Pathways.Mar Drugs. 2024 Aug 30;22(9):395. doi: 10.3390/md22090395. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39330276 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating Effects of Spirulina platensis against Tilmicosin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Mice.Cell J. 2015 Spring;17(1):137-44. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2015.520. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Cell J. 2015. PMID: 25870843 Free PMC article.
-
Renoprotective effect of Spirulina platensis extract against nicotine-induced oxidative stress-mediated inflammation in rats.Phytomedicine. 2018 Oct 1;49:106-110. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.06.042. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30217256
-
Spirulina platensis protects against microcystin-LR-induced toxicity in rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Feb;29(8):11320-11331. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-16481-y. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 34533748
-
Advances in delivery methods of Arthrospira platensis (spirulina) for enhanced therapeutic outcomes.Bioengineered. 2022 Jun;13(6):14681-14718. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2100863. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35946342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ameliorative Effect of Chitosan/Spirulina platensis Ethanolic Extract Nanoformulation against Cyclophosphamide-Induced Ovarian Toxicity: Role of PPAR-γ/Nrf-2/HO-1 and NF-kB/TNF-α Signaling Pathways.Mar Drugs. 2024 Aug 30;22(9):395. doi: 10.3390/md22090395. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39330276 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Potential of Silymarin, Spirulina platensis, and Chlorella vulgaris towards Cardiotoxicity via Modulating Antioxidant Activity, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Rats.Life (Basel). 2024 Oct 11;14(10):1289. doi: 10.3390/life14101289. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adeyemi D. H., Hamed M. A., Oluwole D. T., Omole A. I., Akhigbe R. E. (2024). Acetate attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced cardiac injury via inhibition of NF-kB signaling and suppression of caspase 3-dependent apoptosis in Wistar rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 170, 116019. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.116019 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Afkhami-Ardakani M., Hassanzadeh S., Shahrooz R., Asadi-Samani M., Latifi E., Luther T. (2017). Phytotherapy and phytopharmacology for reduction of cyclophosphamide-induced toxicity in the male urinary system. J. Ren. Inj. Prev. 6, 164–170. 10.15171/jrip.2017.32 - DOI
-
- Agoramoorthy G., Chandrasekaran M., Venkatesalu V., Hsu M. J. (2007). Antibacterial and antifungal activities of fatty acid methyl esters of the blind-your-eye mangrove from India. Braz. J. Microbiol. 38, 739–742. 10.1590/S1517-83822007000400028 - DOI
-
- Ahmed R. A., Alam M. F., Alshahrani S., Jali A. M., Qahl A. M., Khalid M., et al. (2023). Capsaicin ameliorates the cyclophosphamide-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting free radicals generation, inflammatory cytokines, and apoptotic pathway in rats. Life 13, 786. 10.3390/LIFE13030786 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aiba S., Ogawa T. (1977). Assessment of growth yield of a blue-green alga, Spirulina platensis, in axenic and continuous culture. J. Gen. Microbiol. 102, 179–182. 10.1099/00221287-102-1-179 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

